What is a Mockup?
Part 1: What Is a Mockup?
People well versed in making websites or applications know the importance of this component. This might seem like another scary technical term, but this article will help you understand what it is, and where it belongs in the design process.
A mockup is the static design of a website or application. Mockup is more of a skin for an application or website. Since it is a static design and not functional, it may display all the contents, but these functions will not be performed if clicked or tapped on. Mockups have high to mid-fidelity making them closer to the end product. It can be used by the team to view how their idea can be achieved while using the UI designer with a wireframe.

Part 2: Anatomy of Mockup
The anatomy of a mockup generally represents the page or application that it is simulating. Keeping that in mind, during this phase the following things need to be considered:
1. Content Layout
The most important thing on display is the content. The layout of the content determines whether it will attract individuals or not. This layout includes the order in which the content is displayed, the size of the content, and the amount of content displayed on the page or application.
2. Color Usage
The color scheme is another component. Depending on the type of content, choosing the color scheme becomes important. Some content requires more vibrant colors and some a more toned-down set of colors.
3. Typography
You can explore the different typography options you have, and which will suit your page or application. This ranges from font style, size and spacing.
4. Contrast
Usually, a contrast testing tool is used to see how clear your text is in contrast with the background you have set. The more visible your text, the better the contrast settings.
5. Spacing
Negative space might seem bad but in applications and pages, it can serve as a good element. Pages need to be less crowded and clearer in terms of display, spacing makes it possible. Mockups can help deduce the right amount of spacing required.
6. Navigation Visuals
By the time you reach the navigation visuals, the other parts of the anatomy will be finished. The navigation visuals are usually the accessibility or menu bars, an application or page has to easily navigate through the webpage.
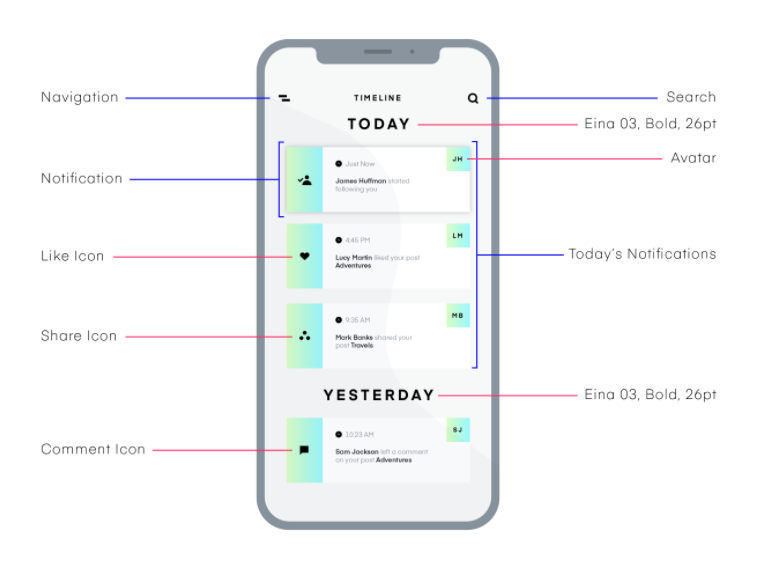
Source: www.invisionapp.com
Part 3: What is the Purpose of a Mockup?
A mockup in similar terms is a mock or simulation of what the original page or application will look like. Since it is a visual draft, it provides the designer to work on different visual options and see which one would work best to bring an idea or wireframe to life.
The designers use this method so that changes can be made to achieve the perfect embodiment of their vision. This means going about and working with the anatomy of a mockup. Checking several fonts, layout, and much more. You can also make a secondary mockup to see which one would look better and then choose the better option. So, mockups bring the layout created by a UI designer of a wireframe to life.
Part 4: Where do Mockups Come into the Web Design Process?
The Mockup lies right at the center of the web designing process if we are to jolt the processes followed. While in retrospect they are still at the very initial stages of a web designing process. A very generic web designing process consists of:
Birth of the idea >> Wireframe >> Mockup >> Prototyping >> Go live.
In a web designing process, the most basic step is the come up with an idea. Once the idea is present a blueprint or layout is created which is known as the wireframe. A mockup builds upon that layout to give it a more lifelike look. Necessary changes to the visual display are made at the mockup stage. Once they are finalized the process is shifted towards prototyping of the page or application. After the prototyping is done and everything is finalized, the page or application goes live.
Part 5: Types of Mockups
The Mockups are divided into 3 types depending on the mode of their creation, this also determines their fidelity.
1. Graphic Design Software
This method is usually implored when designers seek a more pixel-perfect mockup. The fidelity is high for this method giving a better picture of the wireframe.
2. Mockup Apps
There are tools present that help in building Mockups. An example of such an app is UXPin. These tools usually build upon existing experience and templates present.
3. Coded Mockup
These are much more detailed, annotated wireframes and include information about different items available on the page such as dimensions, behaviors, or actions related to interactive content. They are most suitable for documentation. Furthermore, they are the best for handing over to the development team who needs to know every detail of the design. Proper software is required to create high-fidelity wireframes.
Part 6: Tips to Consider While Making a Mockup
Tip #1: Know your Expertise.
As there are three types of mockups you can implore from, know the type you can easily work with. A mockup App works best for beginners as you can use already present templates. Graphic Designing softwares are easy to use as well, but they require expertise too, in order to get pixel-perfect mockups. While finally Coded Mockups should only be implored by people who are confident in their coding abilities.
Tip #2: Having a Clear Idea.
Without a clear foundational idea or vision, you cannot make the perfect mockup that is an embodiment of that vision. Making it necessary that one has a clear idea before working on a layout or wireframe.
Tip #3: Be Creative.
This is the stage where you are bringing your idea to life, make sure that it is as creative it can be. Use the anatomy of the Mockup wisely to make the perfect mockup.
Tips #4: Know the Audience.
It is crucial to know the audience you are trying to target. If your application is for teens, you need to incorporate ideas that would be catchy for the teens. If your application is for another division of society, choose the perfect template that would be best suited for them.
Part 7: Wireframe vs. Mockup vs. Prototype
While working on web design, you will come across these terms quite often. Most people confuse these terms, we will explain their differences so that you do not have to face the same confusion.
Breaking it down into very simple terms, while designing a web page or application, the wireframe acts as a skeleton, the mockup is the skin of that skeleton and the prototype shows the behavior of all this combined.
A wireframe is like a basic blueprint layout with just lines demarcating certain areas and no proper labeling. A mockup is the proper incorporation of fonts, styles, and layouts to have the exact idea of what the end product will look like. The prototype is the exact demonstration of how the application or web page will behave when it goes live.
A wireframe determines the structure, the mockup determines the design while the prototype determines the user interaction before the launching of the application or webpage.
Wireframes help in deriving a structure for the application or webpage. A mockup helps the team in visualizing the end product and making edits to it before prototyping it. A prototype helps in gathering feedback and also helps in developing the product and eradicating its flaws.
Both wireframe and mockup are not interactive, while the prototype is interactive.
All three are linked together, wireframe serves as the basis, the mockup builds upon the base, and the prototype tests it out for user experience.

Source: www.invisionapp.com
Part 8: Example of Mockup
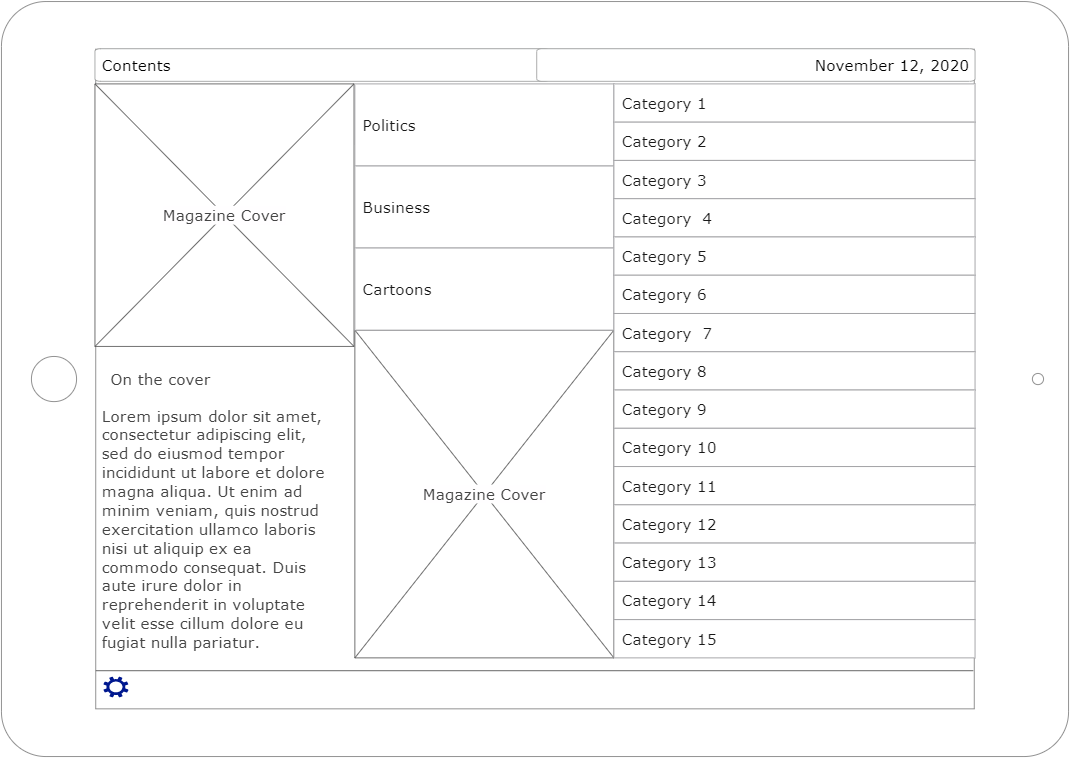
You often need to create a mockup for your product. For that purpose, use EdrawMax’s templates. These templates have all the necessary things you need to create a mockup. Just change it up according to your needs and you’ll be good to go. The template given above is a Map Mockup. Use it to plan how your magazine’s structure will look like.
Part 9: Conclusion
Mockup is one of the most important components of web designing. Having gone through this article, you will have a better understanding of this technical term and where it fits in the web designing process. So, go and get working!

