Waterfall project management is a structured methodology for managing one-way or sequential projects. The process follows a step-by-step approach. Each phase must be finished before the next one starts. If you want to learn and use the Waterfall project management method, then read through the article.
This approach covers the stages involved, such as creating, executing, and managing projects. It will also teach you how to create a waterfall project management tool with EdrawProj. Understand its stages and see how it improves project organization and execution. This article introduces the important principles and practices for successful Waterfall project management.
What Is Waterfall Project Management?
Waterfall project management is a sequential, linear approach to managing projects. It follows a structured flow, progressing through distinct phases—requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance—in a predetermined order. Each stage must be completed before moving to the next, resembling a cascading waterfall, hence its name.
This method best suits industries or projects with well-defined and stable requirements upfront, such as manufacturing, construction, and infrastructure development. It's best where the project scope and objectives remain unchanged throughout the project lifecycle. Waterfall's rigid structure ensures a systematic approach, making it practical for projects with clearly defined deliverables and where changes are less likely to occur once the project has commenced.
Common Stages in a Waterfall Process
The Waterfall project management method consists of distinct sequential stages, each serving a specific purpose in the project's lifecycle:
- Requirements gathering. Project requirements are identified, documented, and analyzed in this initial phase. It involves thorough discussions with stakeholders to understand their needs and expectations. For instance, this stage gathers user requirements, functionalities, and system specifications in software development.
- System design. After defining requirements, the system architecture and design are conceptualized. This phase outlines the system's overall structure, components, and interfaces. For example, in construction projects, this stage involves creating blueprints and designs based on client specifications.
- Implementation or development. With the system design in place, the development phase begins, where the actual product or project is constructed based on the established specifications. This stage involves coding, building, or manufacturing according to the defined design. In software development, programmers write code; this phase consists of assembling components in manufacturing.
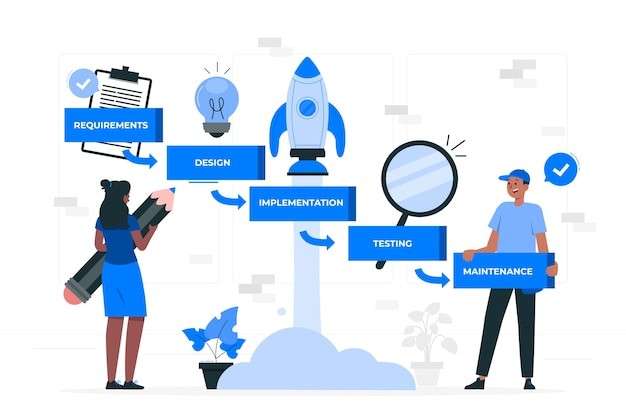
- Testing. Once the product is developed, it undergoes rigorous testing to meet the predefined requirements. Test cases are executed to identify defects, errors, or inconsistencies. In software projects, testing includes unit, integration, and system testing to ensure functionality.
- Deployment or implementation. After successful testing and approval, the product is released or deployed to the end-users. This stage involves delivering the final product or service to the customer or making it operational. In infrastructure projects, deployment consists of the construction's completion and handover.
- Maintenance. The final stage involves maintaining and supporting the product post-deployment. It includes updates, fixes, and support services to ensure the product functions effectively. For example, this phase includes patches, upgrades, and user support in software projects.
The Waterfall model's linear structure allows for sequential progression, where each phase must be completed before moving to the next. However, its strict nature can pose challenges when changes are required, as it's challenging to backtrack once a stage is completed.
When To Use Waterfall Methodology?
As mentioned earlier, the Waterfall methodology is best employed in projects with well-defined and stable requirements, offering clarity and predictability throughout the project lifecycle. It is best for scenarios where the project scope and objectives remain unchanged. Of course, the final deliverable should be clearly understood from the start. Here are instances where utilizing the Waterfall approach is beneficial:
- Predictable projects. Projects with stable, predefined, and unchanging requirements and objectives.
- Traditional engineering projects. Construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure development projects with clear blueprints and specifications.
- Regulated industries. Projects in industries with strict compliance regulations, such as government contracts, where changes must be limited.
- Small projects with clear scopes. Smaller projects with well-understood and straightforward requirements.
However, the Waterfall approach may not be suitable for projects where:
- Uncertainty and changes exist. Projects where requirements are subject to change or not fully understood upfront.
- Innovation and creativity are vital. Initiatives requiring continuous innovation, where flexibility and adaptability are crucial.
- Complex software development. Large-scale software projects where user needs evolve and continuous feedback is necessary.
It's essential to evaluate the project's characteristics, requirements, and stakeholders' needs to determine if the Waterfall methodology aligns with the project's nature before choosing this approach.
Pros and Cons of Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall's structured approach provides clarity and predictability, making it ideal for projects with stable requirements. However, its inflexibility in handling changes and late-stage testing poses challenges. It's especially true in dynamic environments where adaptability and flexibility are essential.
Evaluating project requirements and constraints is crucial in determining if the Waterfall methodology aligns with the project's needs.
In general, here are the pros of using waterfall project management.
- Structured approach. Waterfall's linear and sequential nature offers a systematic structure, ensuring clear project phases and defined deliverables.
- Clear documentation: Detailed documentation is created at each stage, providing comprehensive records of requirements, designs, and development, facilitating easier tracking and management.
- Predictability. Well-defined requirements upfront result in predictable timelines and budgets, offering a clear roadmap for project completion.
- Client involvement. Clients view project progress as each stage delivers tangible outputs, allowing for early feedback and better alignment with expectations.

On the other hand, here are the cons usually associated with using it:
- Limited flexibility. Its strict nature makes it challenging to accommodate changes once a phase is completed. This leads to potential scope creep and cost implications.
- Late testing. Testing occurs at the end of the development cycle, so there's the risk of knowing issues later. It leads to costly rework.
- Adaptability challenges. It's less suitable for projects requiring adaptability or rapidly evolving environments where requirements change frequently.
- High risk of project failure. If initial requirements need to be corrected or understood, it can lead to significant setbacks or even failure. It takes work to make adjustments once the project is implemented.
Using a Tool for Waterfall Project Management
Now, you know all about waterfall project management. What's left is to learn how to implement it. Follow the steps below to create a Gantt chart for Waterfall Project Management. In this guide, you'll be using EdrawProj .
Step 1: Install, download, and launch EdrawProj.
Step 2: On the homepage, click New.
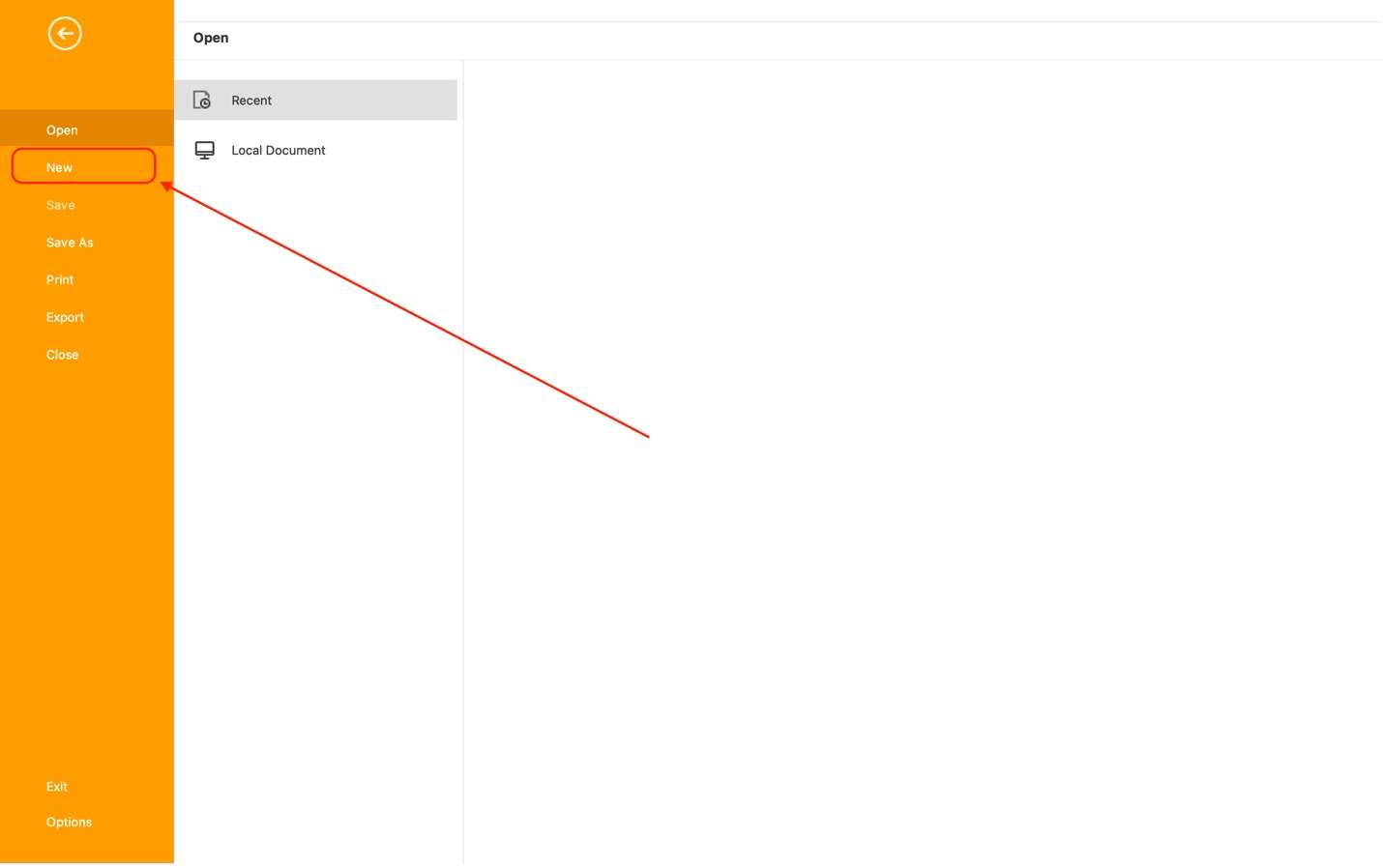
Step 3: In a waterfall project management, remember that each new task must rely on the task before it. Thus, click Add Sub Task when adding a new job.
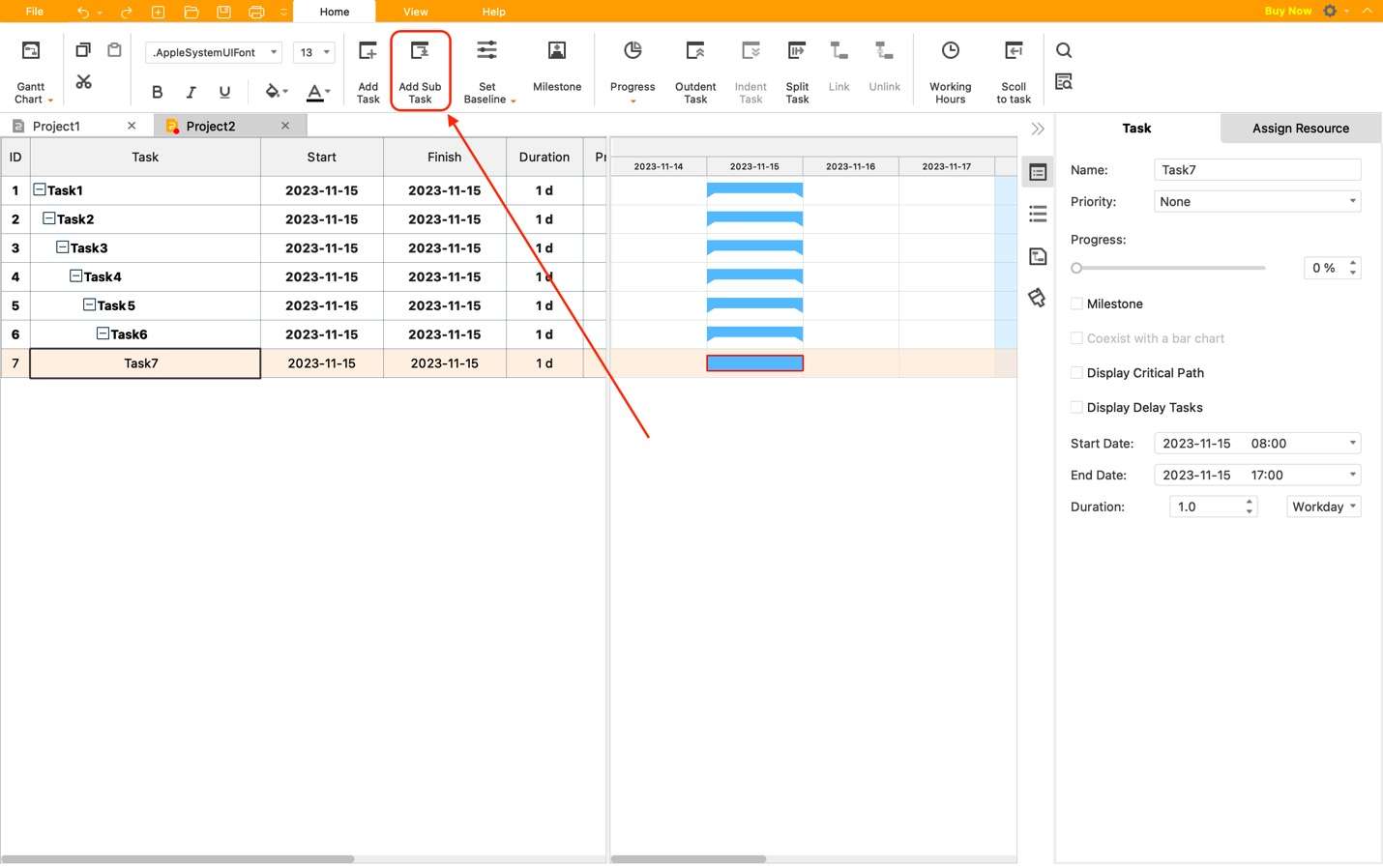
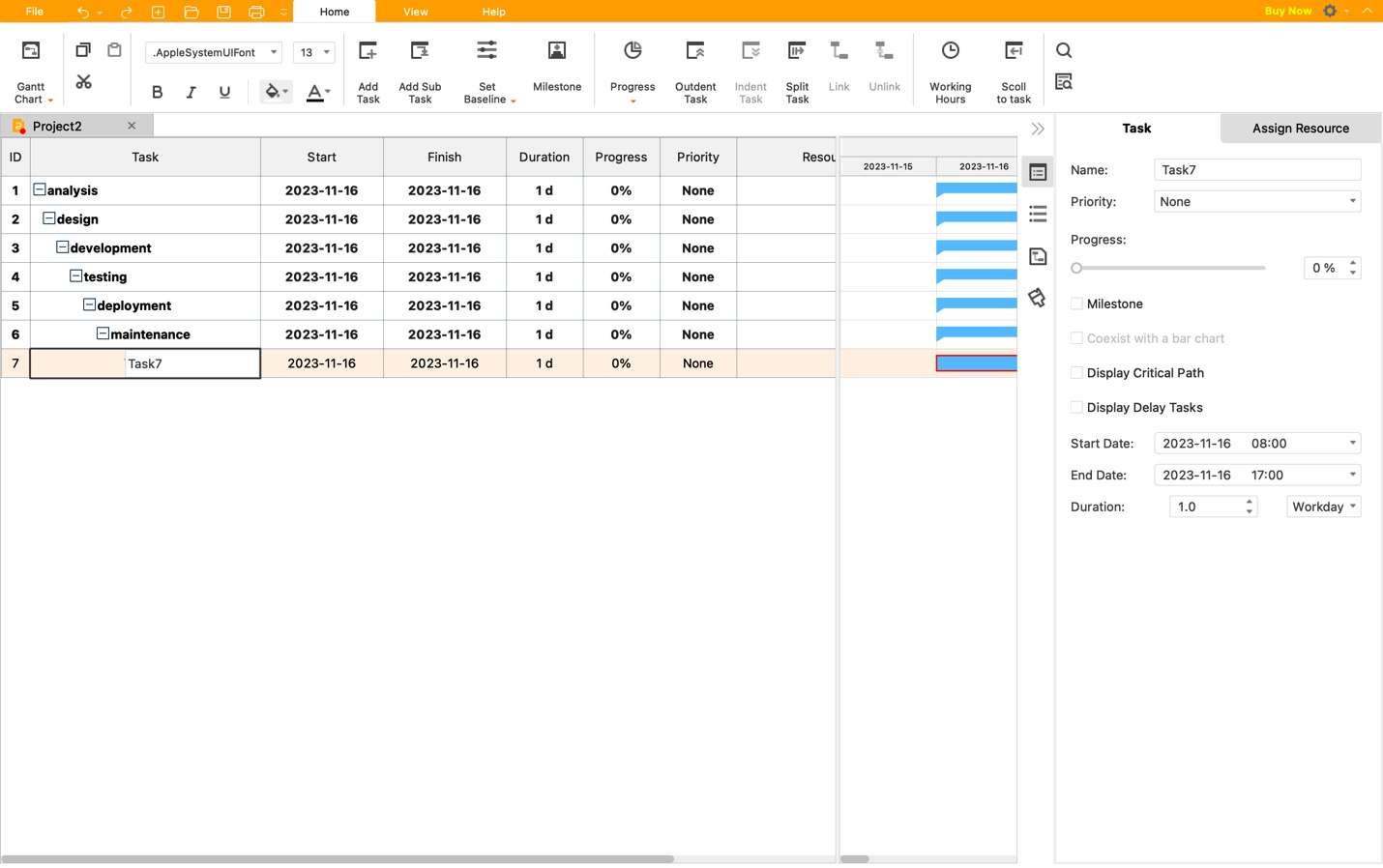
Step 4: Edit the content accordingly. Name tasks under Task and edit dates/deadlines under the Start and Finish columns. You can also check out priority, resources, etc., by scrolling to the right.
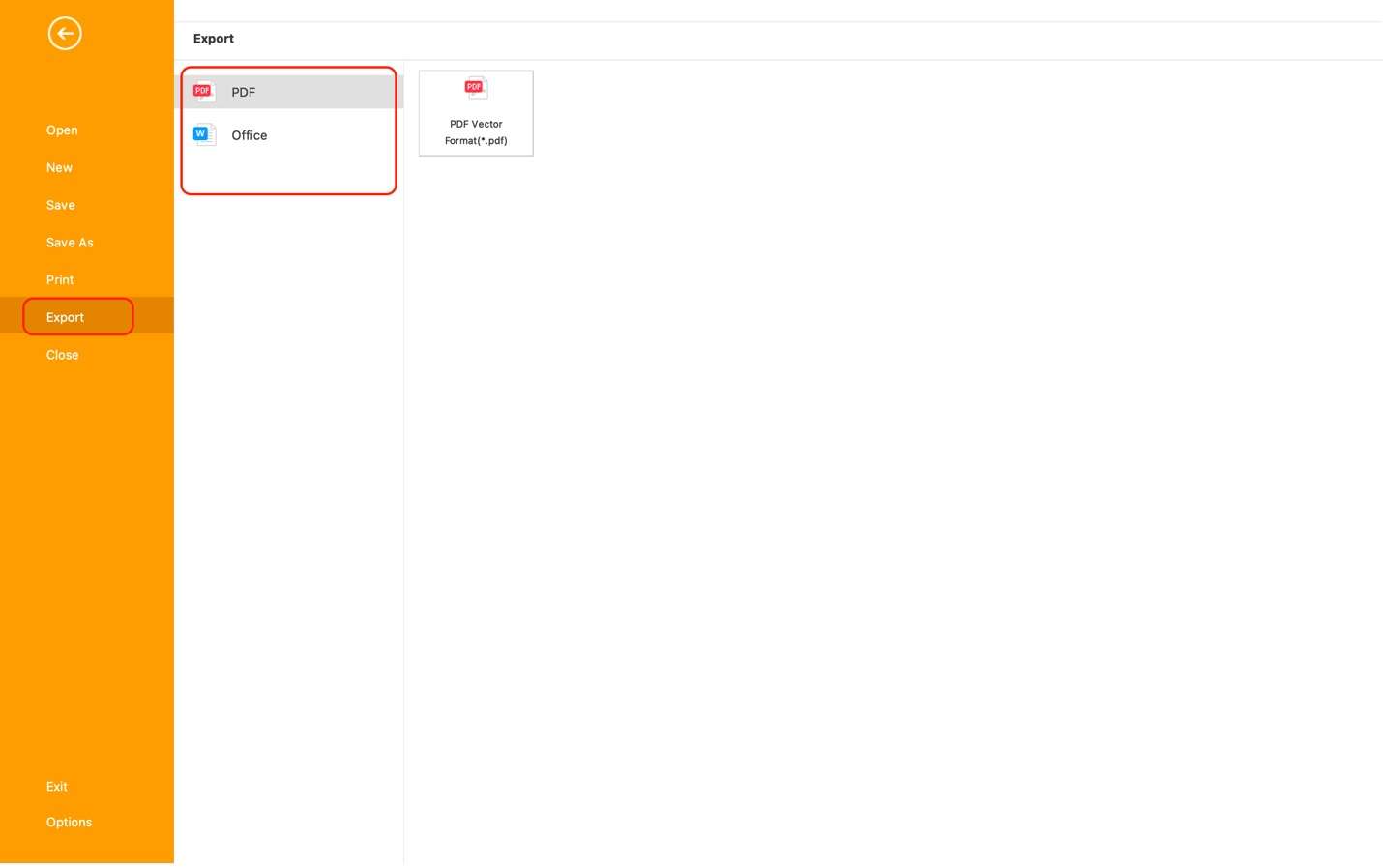
Step 5: After editing the content, you can export the file by clicking File on the menu bar. Then, click Export and choose any of the file types available: PDF or Word.
What Makes EdrawProj the Best Tool for Project Management
EdrawProj is an excellent tool for managing projects because it offers many useful features. It's like a cheaper version of Microsoft Project, easy to use, and perfect for beginners. The program can be used for various industries and satisfies all the needs of project managers. It also covers five major project management scenarios, which is great for flexibility.
Some of its key features include:
- Time management. You can create a personalized work calendar that works for multiple projects.
- Task management. Complex tasks are divided into smaller ones. It helps establish connections between tasks and manages information from different angles.
- Resource management. You can create a resource pool, allocate resources, and monitor their use.
- Progress tracking. Keep track of progress, monitor critical paths and delayed tasks, and compare to initial baselines.
- Project reporting. It allows exporting Gantt charts and generating multiple data reports to analyze project performance.
Conclusion
In summary, Waterfall project management offers a structured roadmap best suited for projects with well-defined requirements. Remember, assessing the project's nature is vital before choosing this method. While the method offers clarity, its inflexibility in accommodating changes poses risks. Consider the project's adaptability needs and complexity to determine if Waterfall fits.
Embrace EdrawProj's tools to navigate the Waterfall stages effectively, ensuring clear documentation and client involvement. Explore and utilize EdrawProj's features wisely for successful project management in line with your project's characteristics and needs.
A professional Gantt chart tool to plan, manage and track your projects, process and resources.