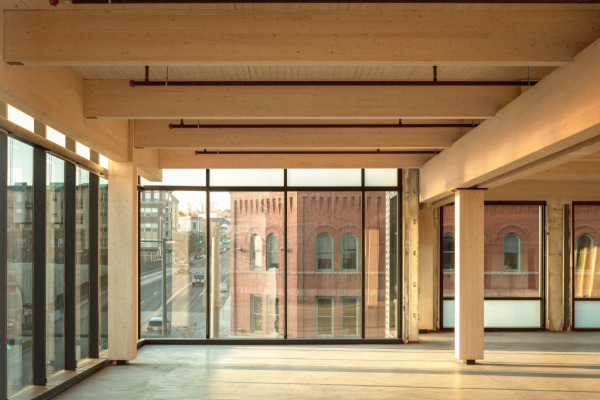
Mass timber utilizes advanced technology to bind wood products using adhesives, nails, or dowels in layered arrangements. This technique produces significant structural components such as panels, posts, and beams, collectively known as mass timber.
These products are exceptionally strong and demonstrate remarkable adaptability in construction, highlighting the innovative capabilities of engineered wood in modern building and construction methods.
The construction industry is increasingly considering mass timber because of its environmentally friendly aspects and structural soundness. These innovatively engineered wood products are sustainable choices for materials and building methods that have a high carbon footprint. By using responsibly fabricated and monitored wood materials, mass timber promotes sustainable forestry practices and reduces the reliance on non-renewable resources.
Additionally, the manufacturing processes for mass timber often result in reduced carbon emissions compared to conventional construction techniques. The off-site prefabrication and production of mass timber components improves construction effectiveness and efficiency as well as minimizes waste on-site. This not only saves time and money but also minimizes the environmental impact of the construction process.
Mass timber construction combines technology, sustainability, and structural innovation, revolutionizing contemporary building design. It offers a more environmentally friendly and efficient alternative to traditional construction methods, making it an attractive option for architects, builders, and developers.
Benefits of Mass Timber
Mass timber construction is gaining popularity in the construction industry due to its numerous value-added benefits. While these construction materials may not be cheap, the cost and long-term benefits make mass timber an attractive option.
Compared to concrete and steel, mass timber columns, beams, and panels are much lighter, resulting in reduced costs of shipping and transportation and also reducing construction Schedules by approximately 25%, leading to significant, timely, and cost-effective projects.
Eco-Friendly
In addition to the financial advantages, mass timber structures have a positive impact on the health and wellness of occupants. The connection to nature that these structures provide enhances the overall well-being of the users, creating environments that promote a sense of well-being.
Carbon Sequester
Another environmental benefit of mass timber is its ability to sequester carbon. Buildings constructed using timber can store carbon throughout their lifespan, and a study shows that a 20-story mass timber building can have a carbon footprint equivalent to removing 3,000 cars from the road annually. This carbon sequestration plays a significant role in mitigating and reducing the ecological impact of building construction.
Timber Sustainability
The use of sustainable practices in sourcing timber is a fundamental aspect of mass timber construction. By prioritizing responsible harvesting, replanting, and continuous growth cycles, modern forestry practices ensure a sustainable supply chain. This helps to meet current timber demands and ensures future growth and resources from the forest. It is important to alternate cutting trees during harvest to allow the remaining trees to gain heights, further improving the environmental sustainability of mass timber.
Structural Strength
Also, a key advantage of mass timber is its structural strength. Multiple solid, load-bearing wood panels are bound together using various techniques such as nailing, gluing, or doweling, resulting in outstanding stability. This combination enables mass timber panels to withstand seismic forces, earthquakes, and high winds, indicating their reliability in extreme weather conditions. This proves to be an extremely important aspect of mass timber.
Fire Resistance
Fire resistance is another critical safety feature of mass timber. Columns, beams, and panels undergo rigorous fire testing to ensure they meet building code standards. Timber burns in a predictable manner, creating a char zone that remains unburned, thus showing fireproof elements on timber, allowing it to maintain a certain degree of structural capacity even in a fire situation.
Engineers innovatively design thicknesses and incorporate additional materials to establish char zones, ensuring that mass timber structures remain structurally sound under fire circumstances. This rigorous approach to fire safety ensures the overall strengths and resilience of mass timber construction.
Types of Mass Timber Framing System
Post-and-beam
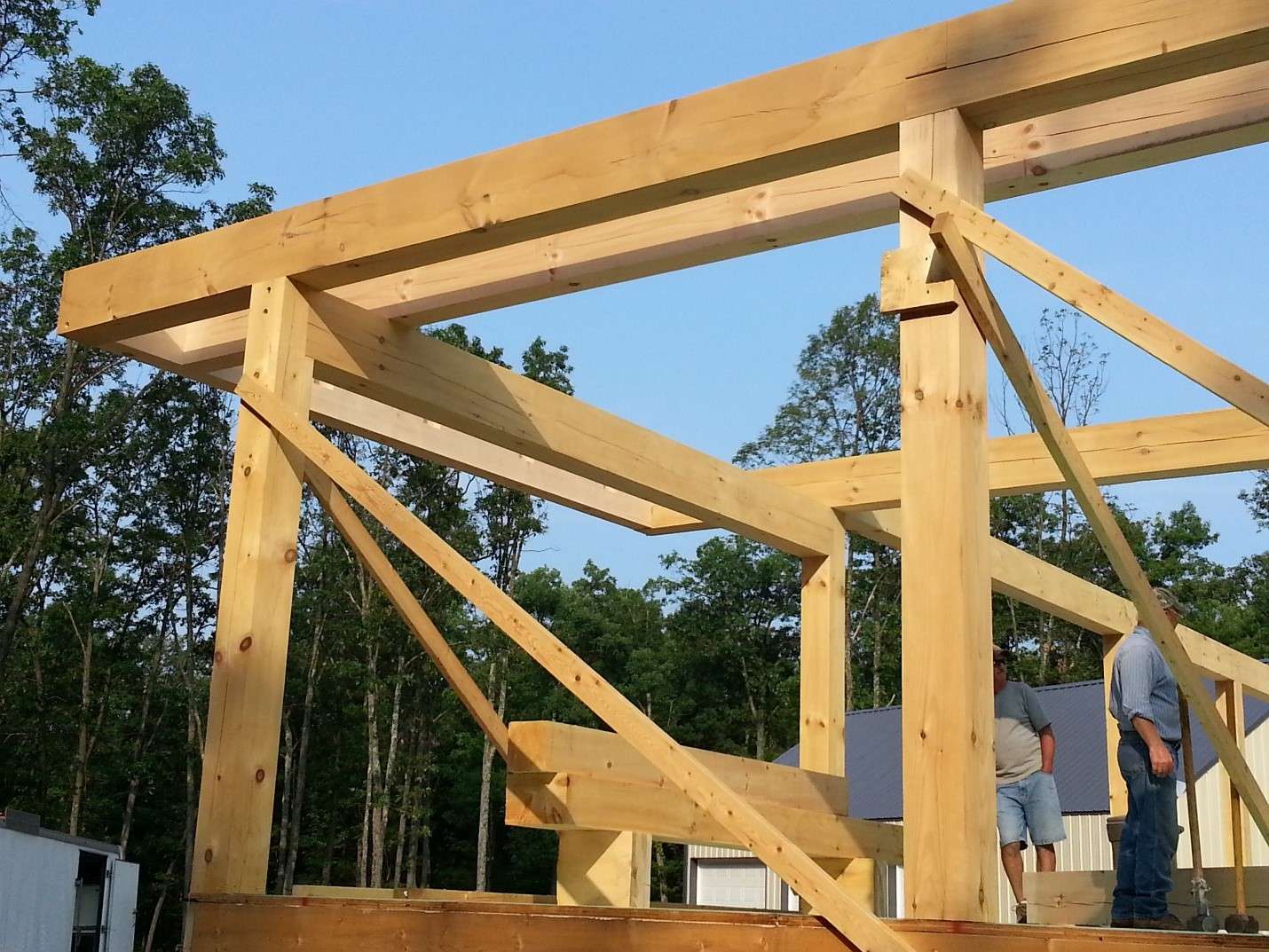

Post-and-beam construction is a timeless method of building that harkens back to the techniques used in ancient heavy timber structures. This type of structural framework consists of posts, beams, and decking that are supported by a foundation. The system utilizes vertical and horizontal wooden members, specifically posts and beams, which are innovatively joined together using automatic steel fasteners.
Post-and-beam buildings rarely depend on load-bearing walls. Often, glued laminated timber (glulam) is used for both the beams and posts, while the decking incorporates numerous mass timber elements such as Nail-Laminated Timber (NLT) and Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT). This style of construction is particularly ideal for open-plan designs, making it a distinguished option for urban commercial buildings and offices.
Mass Timber Floor and Wall Systems
It is crucial to explore the dual functionality of the two-way bridging capability of mass timber. Unlike post-and-beam construction, mass timber floor and wall systems capitalize on the distinctive two-way Bridging capability of mass timber. These platforms are fabricated in a honeycomb arrangement, effectively managing both horizontal and vertical loads.
Sometimes, mass timber can even assume a central role in construction, completely replacing the necessity for concrete. This groundbreaking approach unlocks fresh opportunities in design and construction, presenting a sustainable and aesthetically pleasing alternative to conventional materials.
Hybrid Mass Timber System
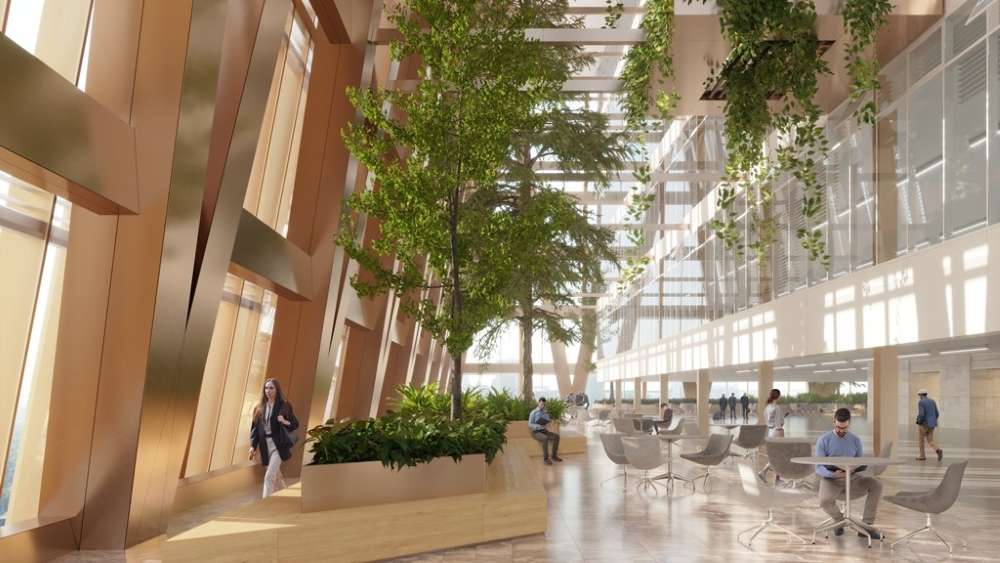

Hybrid mass timber systems are a diverse category that combines steel, wood, concrete, and other building materials and systems. By leveraging the unique strengths and resilience of these materials, hybrid systems offer an extremely high level of flexibility. This flexibility enables a wide range of configurations, including an all-wood solution that incorporates light frame timber construction with mass timber platforms supported by a concrete foundation and steel metal connectors.
The adaptability of hybrid mass timber systems allows for innovative and efficient construction solutions, effectively harnessing the advantages of different materials to meet specific project requirements. Whether incorporating steel, wood, or concrete, these systems show the inherent adaptability and sustainability found in modern construction methods and practices.
Tall Wood Building Construction
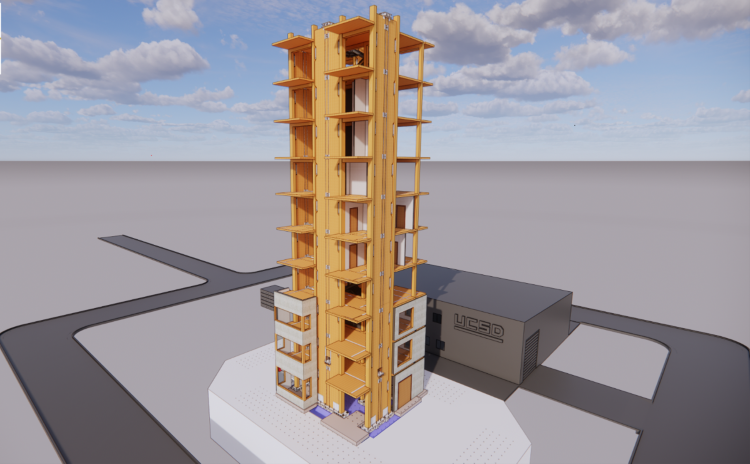

Tall wood construction has become a reality with the introduction of modern mass timber elements like cross-laminated timber (CLT). These buildings, exceeding six stories, incorporate mass timber components as an essential part of their structural support system. This creative and innovative approach is not just a concept but a growing reality as tall wood buildings redefine skylines worldwide.
Equipped with advanced technologies, protection systems, and modern fire suppression, these structures find applications in commercial, residential, and institutional occupancies. They represent a shift towards more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional construction materials. While tall wood buildings up to nine stories existed in the early 1900s, reinforced concrete and steel took over in the mid-century.
However, renewed interest and advancements in mass timber materials and design standards and codes have sparked a reintroduction and resurgence in tall wood construction. Architects and engineers now have access to innovative technologies such as CLT, glued-laminated timber (glulam), and structural composite lumber (SCL), which expand their innovation and capabilities in constructing tall wood structures.
The study and research support the safety, structural resilience, energy efficiency, and durability of mass timber, aligning with fire protection standards and codes. Organizations like FP Innovations play a crucial role in providing technical knowledge and resources, such as CLT design handbooks and guides for tall wood building design and construction. This empowers structural engineers and designers to embrace mass timber in their projects.
The emergence of tall wood buildings signifies a transformative era in sustainable construction. These structures not only shape skylines but also meet stringent safety and performance standards, making them a promising choice for the future of building design.
Difference Between Mass Timber and Tall Wood Construction
Mass timber construction and tall wood construction are related concepts, yet they differ in their scope and application within the realm of modern building techniques. Mass timber construction is a broader term that encompasses a variety of engineered wood products like cross-laminated timber (CLT), glued-laminated timber (glulam), and laminated veneer lumber (LVL).
On the other hand, tall wood construction specifically pertains to the height of the building. Tall wood construction is defined by its vertical scale, typically exceeding six stories, where mass timber components play a pivotal role in the building's structural framework. The emphasis in tall wood construction is on the utilization of mass timber elements, such as CLT, to support the vertical load-bearing requirements of a multi-story building.
Essentially, while mass timber construction addresses the general use of engineered wood products in construction, tall wood construction narrows its focus to the vertical dimension, highlighting the application of mass timber in the context of building height, often associated with environmentally friendly and sustainable building practices.
A professional Gantt chart tool to plan, manage and track your projects, process and resources.