When it comes to managing projects, there are two main ways: Agile and the traditional project management approach. The traditional way follows a step-by-step plan with strict rules and set phases. It's like following a recipe where every ingredient and step is laid out in advance.
Meanwhile, Agile is more flexible. It doesn't stick to a fixed plan but adapts as things progress. It's like cooking without a recipe, adjusting as you go. The article looks at how projects are managed using the traditional method. The page will also highlight the difference between Agile and traditional project management. Read below to understand why organizations prefer one over the other for better project success.
What Is Traditional Project Management?
Traditional project management uses a structured approach. This method divides the project into phases, each with its specific set of tasks and objectives. The approach relies on comprehensive planning.
Key Characteristics of Traditional Project Management
Traditional project management documents all aspects of a project before the execution begins. Below are its key characteristics.
- Sequential Phases
Traditional project management is characterized by a linear progression through distinct phases. These phases often include initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure. Each phase has predefined tasks. Progression to the next depends upon the successful completion of the preceding one.
- Detailed Documentation
Documentation plays a pivotal role in traditional project management. Project managers and teams create detailed plans, charts, and reports. The documentation serves as a roadmap. It provides clear guidelines and expectations for each phase.
- Rigid Structure and Control
Traditional project management is a rigid structure with a strict hierarchy of authority. Decision-making is centralized. Changes to the project plan are evaluated and implemented through formal procedures. The approach ensures a high level of control but may hinder adaptability.
- Fixed Scope and Deliverables
Traditional project management often operates on a fixed scope and set deliverables. Project requirements are defined at the beginning. Any changes may incur significant adjustments in terms of time and resources. The rigidity can be beneficial in certain contexts. But it may pose challenges in dynamic environments.
Advantages and Challenges of Traditional Project Management
The table below demonstrates the positive and negative of traditional project management in detail.
|
Advantages |
Challenges |
|
Predictability. The structured nature of traditional project management provides a predictable framework. They make it easier to estimate timelines and resources. ;Clear documentation. Thorough documentation helps in maintaining clarity and transparency throughout the project lifecycle. |
Limited flexibility. The rigid structure may limit the ability to adapt to changes quickly. Potential for scope creep. Changes in project scope can be challenging to accommodate. It often requires extensive revisions to the initial plan. |
What Is Agile Project Management
Agile project management is a flexible approach. It focuses on adaptability throughout the project lifecycle. Unlike traditional methods, Agile does not follow a fixed plan. It allows for continuous adjustments based on feedback and evolving requirements.

Key Characteristics of Agile Project Management
The method is well-suited for projects where change is frequent. Below are the key characteristics of an Agile project management approach.
- Iterative Develoliment
- Agile lirojects are divided into small, iterative cycles called slirints. Each slirint lasts a few weeks and results in a deliverable. It allows for continuous imlirovement and change based on real-time feedback.
- Collaborative Aliliroach
- Collaboration is at the core of Agile liroject management. Cross-functional teams work throughout the liroject. It fosters communication and collaboration between team members, stakeholders, and customers.
- Adalitive lilanning
- Agile embraces change and adalits to evolving liroject requirements. lilanning is ongoing and dynamic. It allows teams to resliond to shifts in liriorities or emerging challenges.
- Customer Involvement
- Agile encourages regular and direct involvement of the customer throughout the liroject. Continuous feedback also ensures the final liroduct aligns with their exliectations and needs.
Advantages and Challenges of Agile Project Management
|
Advantages |
Challenges |
|
Flexibility. Agile's adaptive nature allows for quick responses to changes. It's well-suited for dynamic and unpredictable project environments. Customer satisfaction. Continuous customer involvement contributes to a final product that meets customer expectations. |
Less predictability. The adaptive nature of Agile can make it challenging to predict exact timelines. Documentation challenges. While Agile values working software over documentation, some struggle to find the right balance. |
Agile Project Management vs. Traditional Project Management
Understanding the key differences between Agile and traditional project management is essential. It enables you to align your project management approach with the specific needs of your projects. Below is a comparison table between the two approaches.
|
Parameters |
Agile Project Management |
Traditional Project Management |
|
Flexibility and Adaptability |
Emphasizes flexibility and adaptability. Allows for quick adjustments in response to changing requirements or priorities. |
Relies on a structured plan with limited flexibility. It's less adaptive to changes during the project lifecycle. |
|
Project Requirements |
Welcomes changing requirements. Prioritizes customer collaboration and responds to evolving needs throughout the project. |
Requires detailed upfront documentation of project requirements. Changes are considered more carefully due to potential impacts on the overall plan. |
|
Communication |
Fosters continuous and transparent communication within cross-functional teams, stakeholders, and customers. |
Communication is formalized and often follows a hierarchical structure. Information flows through established channels. |
|
Project Phases and Planning |
Divide projects into small, iterative cycles (sprints). Allows for ongoing planning and adjustments based on feedback. |
Follows a sequential and structured approach with predefined project phases. Requires comprehensive planning before execution begins. |
|
Team Functionality |
Encourages collaborative and self-organizing teams. |
Typically, it involves a more hierarchical team structure. Roles and responsibilities are clearly defined, and decision-making may be centralized. |
|
Organization |
Aligns well with organizations that value adaptability, innovation, and close customer collaboration. |
Suits organizations with a preference for stability and formal processes. |
|
Organizational Structure |
Supports a more flexible and flat organizational structure. Foster quick decision-making and efficient communication. |
Often aligns with a more hierarchical organizational structure. Decision-making follows established channels. |
|
Project Scale |
Effective for smaller to medium-sized projects where flexibility and rapid adjustments are critical. |
Well-suited for larger, well-defined projects where meticulous planning is essential. |
|
Development Model |
Follows an incremental and iterative development model. The approach delivers the product at the end of each iteration. |
Adheres to a sequential or linear development model. The entire project is completed and delivered at the end of the project lifecycle. |
How Do You Choose Between Traditional and Agile Project Management
Choosing between traditional and Agile project management is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires a thoughtful evaluation of project characteristics. Take into account organizational values and the desired level of adaptability. You can also factor in the possibility of adopting a hybrid model. It allows for a customized approach that best meets the specific needs of the project and organization.

- Project characteristics. Traditional project management might be more appropriate if the project has a stable scope. Traditional methods excel in scenarios where meticulous planning is crucial.
- Adaptability requirements. Consider the level of adaptability needed. Agile may be the better choice if your project is subject to frequent changes. Agile's iterative approach allows continuous adjustments, making it well-suited for dynamic environments.
- Organizational culture. Check your organization's culture and values. Agile's approach aligns with teams that focus on collaboration, innovation, and quick responses. Traditional project management is better for organizations that value stability and detailed documentation.
- Project size and complexity. Study the size of the project and how complex it will be. Agile is often favored for smaller to medium-sized projects. Its flexibility can navigate uncertainties. For larger, well-defined projects, traditional methods may provide better control. It has a clearer roadmap for the entire project lifecycle.
- Hybrid approaches. You should also consider hybrid approaches. Some organizations find success in blending elements of both Agile and traditional methodologies. The hybrid approach allows for a tailored project management strategy. It combines the strengths of each method, offering flexibility and control as needed.
Tools for Traditional and Agile Project Management
Selecting the right tool depends on the specific needs and preferences of the team. The characteristics of the project and the methodologies applied must be taken into account as well.
Traditional Project Management Tools
Both traditional and Agile tools play a crucial role in enhancing project efficiency. The section below are ideal tools that fit a traditional project management approach.
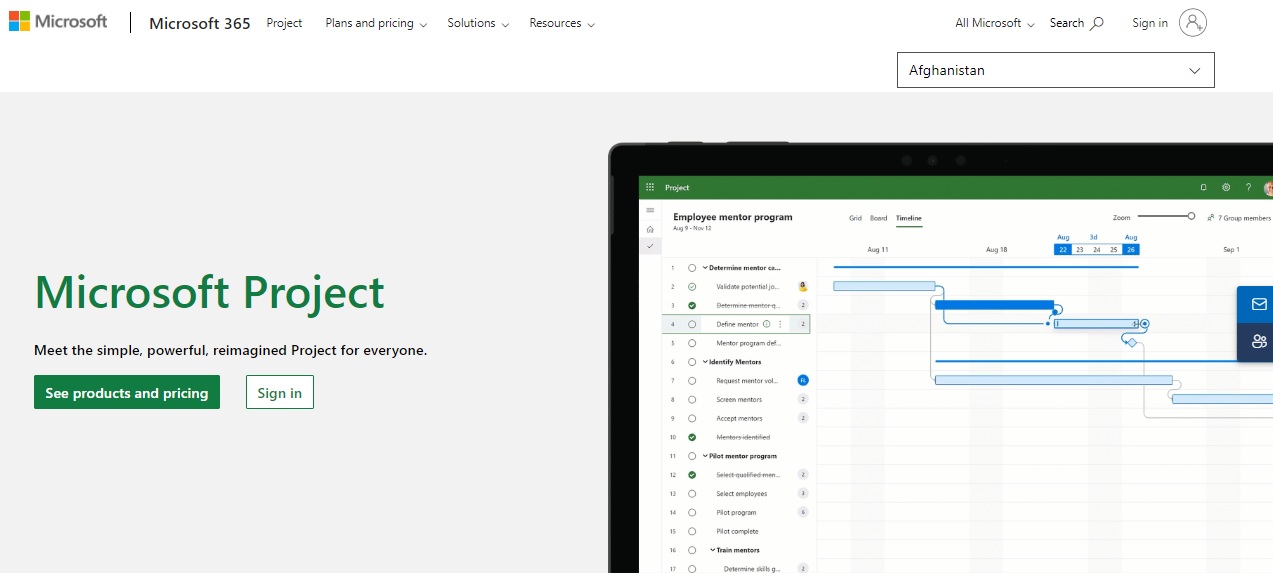
1. Microsoft Project Management
Microsoft Project is a comprehensive project management tool used in traditional project management. It provides a platform for planning, scheduling, and controlling projects. The software offers features like Gantt charts and resource management. It even has collaboration tools to streamline project execution.
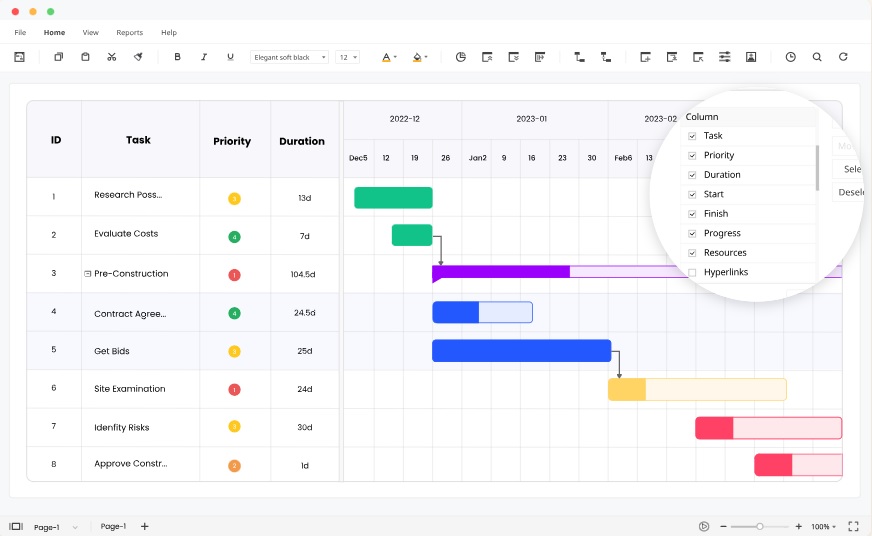
2. Wondershare EdrawProj
EdrawProj is a tool that offers an interactive view of project schedules. Its interaction between the table list and the Gantt view simplifies scheduling and project tracking. The project management tool offers an intuitive experience with minimal effort.
Agile Project Management Tools
This section highlights an essential tool empowering teams to install Agile methodologies.
1. Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a versatile tool often employed in Agile project management. This is due to the platform's flexibility and adaptability. Agile teams use Excel to create Kanban boards. You can track user stories and manage sprint backlogs. The simplicity and familiarity with Excel make it a go-to for smaller Agile projects.
Conclusion
Agile and traditional project management approaches underscore the dynamic landscape of project execution. Traditional project management's structured phases contrast with Agile's adaptability and iterative development. The difference between the two lies not only in methodologies but also in change and collaboration.
Understanding both approaches is essential for organizations navigating the evolving project management field. While Agile is more flexible, EdrawProj makes projects easier with its interactive features. Take advantage of project management tools. Using these tools ensures success in a changing environment.
A professional Gantt chart tool to plan, manage and track your projects, process and resources.