The Complete Guide to Database Schema

In this guide today, we will discuss what database schema is and what are its different types. Moreover, we will also discuss the role of the database schema in a database management system and its integration requirements.
So, let’s dig right in!
What is a Database Schema?
The database schema represents any structure that we are finding around the data. It includes tables, views, fields, relationships, packages, procedures, indexes, functions, types, sequences, materialized views, triggers, queues, synonyms, database, links, XML schemas, and other elements.
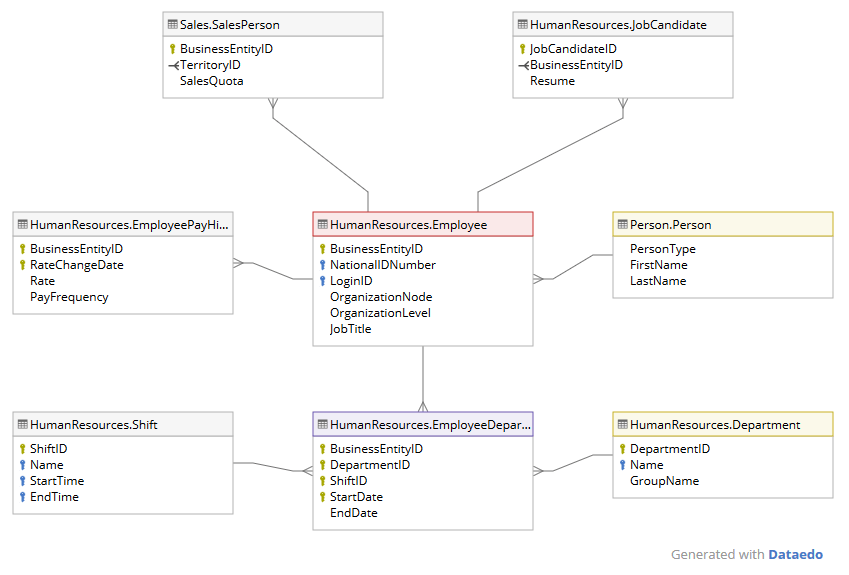
Image source: dataedo.com
The schema database helps you access the data in an organized and efficient manner. For example, you have multiple files containing all types of data and it will take you a lot of time and effort to find what you are looking for.
To understand and access the data efficiently, it is important to create a structure. that structure and its corresponding relationships are what we call all the database schema.
Types of The Database Schema
There are three main types of database schema:
1. Physical Schema
The design and layout of a database at the physical level are called physical schema. It shows how data is stored in blocks of storage.
2. Local Schema
The design of a database at a logical level is called a logical schema. Professional database administrators and programmers work with the logical schema. The data at this level is presented in data records stored in data structures, but the internal details like the implementation of the data structure are unknown.
3. View Schema
The design of the database at the view level is called view schema. This means that the database is ready for user interaction with the database system and describes how it will impact the user.
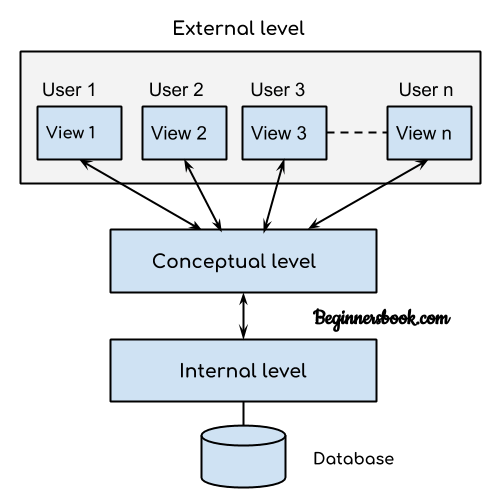
Image source: beginnersbook.com
Apart from these basic types of the database schema, certain patterns have developed over time. Based on these patterns, here are some types of database schema:
1. Star Schema
It is the simplest database in which one or more fact tables are linked to multiple dimension tables. It is suitable for simple queries.
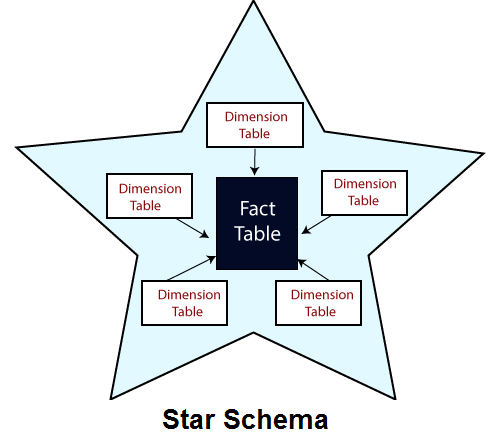
Image source: javatpoint.com
2. Related Snowflake Schema
Snowflake schema represents a multidimensional database where the dimensions are normalized into two separate tables, creating an expansive network of snowflake-like structure.
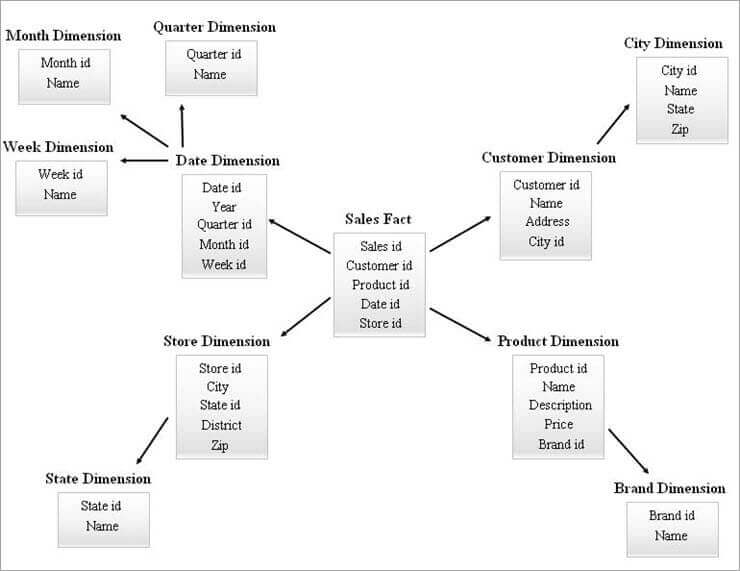
Image source: softwaretestinghelp.com
Instance and Schema in DBMS
Database instance and database schema in the database management system (DBMS) are related, but they do not mean the same thing.
The database schema is the structure of a database and designed when there is no database at all. Once the database is operational, it becomes very hard to make any changes to the database's design. So, at the designing stage, the database schema is the layout of a plant database that does not contain any actual data.
On the other hand, a database instance is a snapshot of the database that existed at a particular time. It represents the state of an operational database with data present at any given time.
This means that the database instances change over time, whereas database schema remains static because it is difficult to change a database's structure once it is operating.
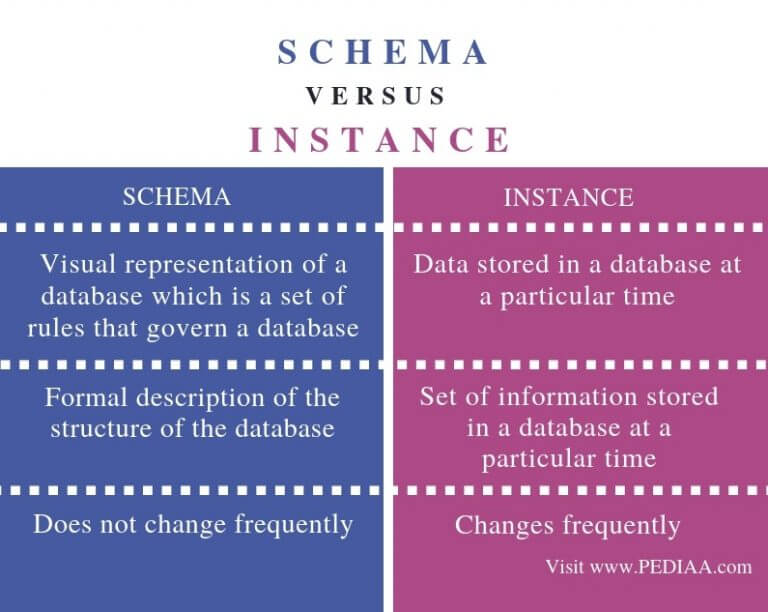
Image source: pediaa.com
Database instance and schema affect each other in DBMS, but the system shows that every instance complies with the structure in the post by database designers in the schema. In this way, the DBMS makes sure that every instance is in a valid state by following all the validations, conditions, and constraints that the database imposes.
Schema Integration Requirements
Schema integration refers to integrating multiple sources into a single schema. By following certain requirements, you can influence the detailed structure of the schema. While all the integration requirements are not necessary, they are important for a seamless and ideal transition.
Here are database schema integration requirements:
• Minimality
Thus requirement demands that none of the elements should be lost in any of the resources.
• Normalization
Independent entities and relationships should not be put together on the same table in the schema.
• Overlap Preservation
Every overlapping element that is to be integrated should be in the database schema table.
• Extended Overlap Reservation
Elements only appearing in one source but associated with overlapping elements should be copied to the resulting schema.
EdrawMax
All-in-One Diagram Software
- Superior file compatibility: Import and export drawings to various file formats, such as Visio
- Cross-platform supported (Windows, Mac, Linux, Web, Android, iOS)


