What is Deming Cycle?
Edraw Content Team
The Deming Cycle is one of the renowned tools for quality improvement that has been in vogue in international companies worldwide. It helps to plan for improvement on a continuous scale in different contexts such as manufacturing or service companies as well as in educational or learning processes.
What is the Deming Cycle?
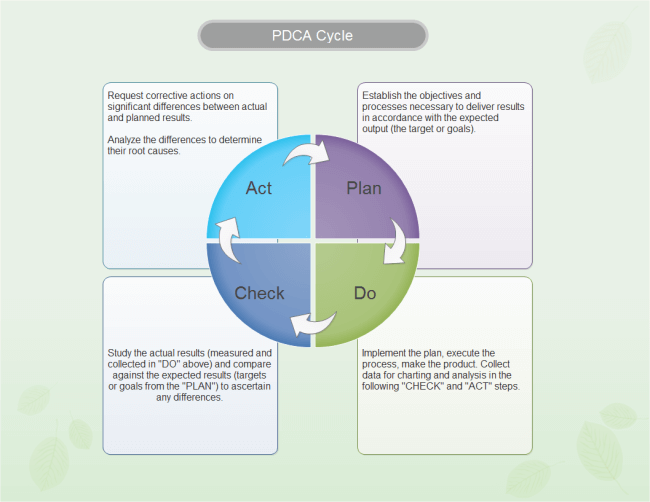
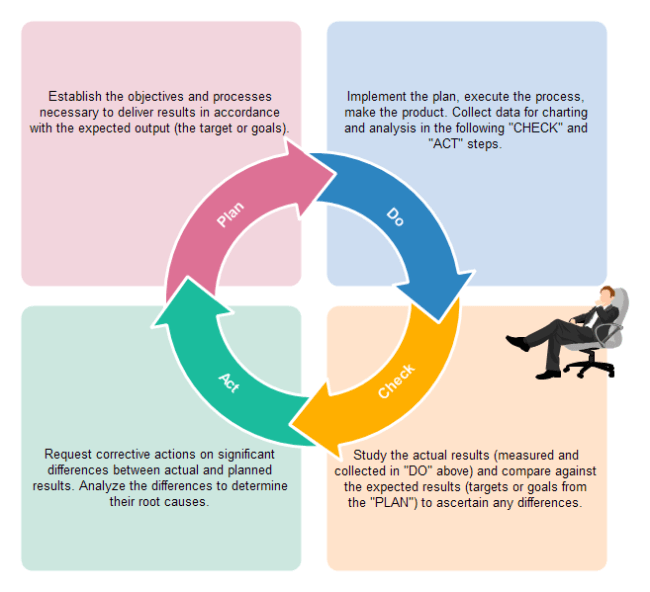
The Deming Cycle is also known as the PDCA cycle. It is a model for continuous improvement of quality which comprises logical sequences of four steps that are repetitive to help in bringing on continuous improvement as well as learning. The four components of the cycle are known as PDCA or Plan, Do, Check or Study and Act. It is also called the Deming Wheel since it is a spiral that leads to continuous improvement.
Quality experts J.M. Juran and Deming implemented his method in several Japanese companies and used statistics to showcase how well this cycle works. In general, the Deming Cycle comprises the following steps:
- Plan – Planning ahead for change, analyzing and predicting results.
- Do – Executing the plan.
- Study – Checking and examining
- Act – Taking action in order to improve or standardize a process.
There are several applications of the PDCA cycle. It can help to manage the daily routines and activities of an individual as well as a team. It helps to streamline problem-solving, project management, can act as a tool to plan for continuous development, for vendor development, development of products and human resources and so forth.
History of Deming Cycle
With regard to Deming Cycle and its origin, it was named after an American engineer and statistician Deming who later on became a management consultant. Having started as work in electrical engineering fields, he is known for the works he did in the auto industry in Japan after the Second World War.
He championed statistical process control procedures. He was also influenced by the works of Walter Andrew Shewhart who published his findings of a statistical method in the late thirties. Shewhart cycle was a concept of looking into improving the steps of mass production processes. Deming Wheel was built off this concept and was debuted in the fifties. He stressed that there should be constant interaction between sales, research, design and production processes.
What are the Purposes of the Deming Cycle?
There are different ways to implement the Deming Cycle or PDSA helps to improve any product or process by breaking the improvement cycle down into small steps. It is effective when one wishes to initiate Six Sigma or Total Quality Management which are usually projects taken up for quality control and improvement. Deming Cycle example can also help explore different solutions that are available for a problem and such changes can occur in a controlled manner with PDCA.
The purpose of this cycle can also be to avoid resource wastage. If a solution is ineffective and rolled out, then wastes often take place. However, in a controlled environment, it can help to see the effectiveness of a solution. The model also applies to different business environments, from project or product development, product lifecycle, supply chain management and so forth.
Examples of Deming Cycles
There are several instances of using the Deming Cycle. For instance:
Improving efficiencies by integrating different business processes, here PDCA would comprise of four phases in the following ways in Deming Cycle example:
- Plan – Identify the problem and analyze process inefficiencies.
- Do – Implement the solution on a small scale.
- Check – Set benchmark for checking new processes against the old.
- Act – Find the right solution and implement it across the organization.
How to Improve Sales for a Company?
PDCA can be implemented in the following ways for checking and improving sales of a company.
- Plan – Identify the whys as to sales being down and how to improve the same.
- Do – Implement solutions in a small way.
- Check – Set benchmarks to check improvements in new processes against the old.
- Act – Choose the right solution and implement worldwide.
How to Implement the Deming Cycle?
With the help of Edraw software, one can implement the Deming Cycle easily for different business process improvement situations. They offer a diagram creator for PDCAs or plan do check act diagrams that are easily created with such software.
Steps to create such diagrams using such software are the following:
1. Download the Right Version
The software is available for Windows and Mac versions as well. Being easy to download and use, one can simply get started once the software is installed in their system.
EdrawMax
All-in-One Diagram Software
- Superior file compatibility: Import and export drawings to various file formats, such as Visio
- Cross-platform supported (Windows, Mac, Linux, Web)
2. Start Using Library Templates
This is the next step to do when you start to draw the cycle. One can find readymade shapes in the library panel. Besides the shapes one can also look at premade and rich templates that help a user modify the different structures; this helps them get their diagrams started easily.
3. Use Formatting Tools
Small tools are available that can be used for formatting; with this one can easily arrange, group, rotate and align the different objects in their diagram.
4. Themes and Effects
There are themes available with different effects; these can be easily added and a theme changed with a few clicks; one can also edit the text fields, images, and photos.
5. Easy Export
There are easy ways to export the diagram to different applications and in different formats such as PDF, PPT, PowerPoint, BMP, JPEG, and others.
The software suite is available free of cost and can be used easily, even for those who are drawing up a plan do check act diagram for the first time.
Weaknesses of the Deming Cycle
There are certain limitations of the Deming Cycle such as:
Allowing for Variables
It is a step by step process; it works best when conditions are predictable. If a project involves variables then the cycle cannot account for the same.
Emergency and Speed
When the four steps are being implemented in a Deming Cycle example, progress is slow. Cycles come in certain methods and operational plans and cannot be implemented swiftly.
Paralysis by Analysis
If a project is being analyzed at the early stages it can be paralyzed for a long time. Careful planning is part of the process and real work starts only in the action phase.
Not Focused on Results
End results are not looked at in Deming Cycle example. Here it is more about quality control and can be slow when it needs to keep up with the changing needs of clients or to produce certain results.
Organizational Issues
Those who plan and those who are given to implement the process changes might bring in a divide. It is also difficult to assess the performance of individuals since it focuses on teamwork and collaborative efforts.
Key Takeaways
Deming Cycle is one of the long-tested quality control processes or methods that have helped automobile and other industries streamline their processes by identifying quality control issues and measures. With software solutions like EdrawMax it is possible to draw up any Deming Cycle example and create a professional finish on such a diagram.