Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
If you are looking for an ideal business modeling diagram for your business, then Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is the ideal choice. BPMN has been designed to be an easily comprehensible diagram by all business stakeholders, including business managers, technical developers, and business analysts. It helps avoid communication gaps by using common language to describe the entire processes in a business system.
In this article, we will discuss all the key things that you need to know about BPMN, including:
What is a BPMN Diagram?
BPMN is an open standard notation that utilizes visual modeling language or diagrams to define business process workflows. This visual modeling language help specify enterprise process workflows through its intuitive business analysis applications.
This visual Diagram is ideal mainly for business applications, thanks to its prevalent and intuitive graphical flowcharts that are easily understandable by all business stakeholders.
Purpose and Benefits of a BPMN Diagram
Just like any other project management tool, BPMN has multiple uses and benefits to different fields but, more importantly, to business processes. Some of its major benefits and purposes include:
Purpose
- Process managing: to monitor and control the processes
- Process implementation: which is ideal for technical experts
- Business analysis: to improve business processes
Benefits
- BPMN helps bridge the communication gap that often transpires within business process design and implementation.
- To provide an easily understandable standard notation (to all business stakeholders).
- It is a powerful tool that can analyze and display probable intricacies within any business processes.
- Through Business Process Diagrams, BPMN equips businesses with the ability to define and understand their business procedures.
Types of BPMN Application
BPMN is used in business groups with a wide variety of targeted audiences. BPMN can cover this wide range of usage to allow the diverse audience of the Diagram to be able to easily understand the process.
There are three basic types of uses of BPMN:
1. Private Business Processes / Internal Business Processes
This type of BPMN is internal to a specific organization. It is also called workflow or BPM processes. This type of BPMN doesn't cross pools or organizational boundaries. If swim lanes are used in this kind of BPMN, then the Sequence Flow of the Process will be contained within a single Pool and cannot cross the boundaries of the Pool. Message Flow can cross the Pool boundary to show the interactions that exist between separate private business processes.
2. Abstract Business Processes / Public Business Processes
This type of BPMN is between a private process and another participant or process. The abstract process only includes the activities that are applied for communicating outside the private business process. Abstract processes are contained within a Pool to show the Message Flow between the abstract process activities and other activities.
3. Collaboration Business Processes / Global Business Process
This type of BPMN shows the interactions between two or more business activities. Collaboration processes are contained within a Pool and the different participant business interactions are shown as Lanes within the Pool.
Business Process Model and Notation Symbols and Elements
The main elements and symbols of BPMN are as follows:
- Flow Objects: Activities, Gateways, and Events.
- Swimlanes: Lane or Pool
- Artifacts: Annotation, Data Object, and Group.
- Connecting Objects: Association, Sequence Flow, and Message Flow
So, let's now look at what each element and symbol look like and what it represents.
Activities
Activities are elements or symbols used to represent the tasks to be completed by a process. The sub-processes, multiple instances, compensation, and loops, can be added to make them more detailed.
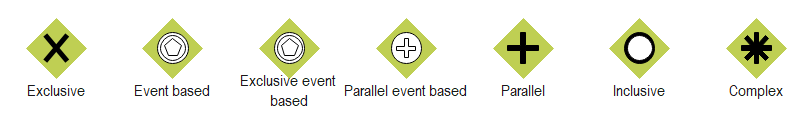
Gateways
Getaways are also known as conditional elements and are denoted by diamond symbols. It comprises different types, as shown below, and used as a decision point to alter paths based on diverse situations and events.
Events
An event is referred to as the happening of something. This element features three different sub-elements that provide detailed use for each element. They comprise of starting, intermediate, and end, as shown in the picture below.

Association
Associations are specifically used to link a text or event to a getaway or business and are usually denoted by dotted lines. In other words, it is used as a "tying" element.

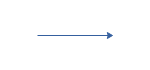
Sequence Flow
This element is denoted by a straight line that ends with an arrow. It is used to show sequence flow or pure flow of work from one stage or process to another.
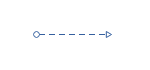
Message Flow
This symbol signifies the way work gets done in different departments or companies. Therefore, Message Flow is a "not a strict action" element, and it is denoted by a dashed line with an arrow at the end and a circle at the beginning.
Artifacts
The group, data object, and annotation are considered to be artifacts in a BPMN diagram. Furthermore, they are extra information that developers provide to improve a BPMN diagram. Each of these artifacts stands for:
- Data Object: Illustrates the required data for an operation
- Group: It doesn't change the Diagram's flow but is taken as the grouping of activities and logical formation.
- Annotation: An additional explanation to be used as part of the Diagram

Lanes
Lanes can be used in several ways within a BPMN diagram. First, it can be specific positions or general roles in different organizations. However, it can sometimes be used to show each department's tasks and responsibilities by denoting them as parallel within the process. Lanes are actually considered one of the prominent elements.

Pool
Pools are considered the most substantial units on a BPMN diagram. Pools show participants like firms, businesses, or departments. But more importantly, they help show business processes workflow upon which they get done.

How to make a BPMN Diagram in EdrawMax
EdrawMax is one of the most effective software and tool that can be used to Diagram different types of charts and diagrams, such as business process modeling diagrams. In this part, we will be reviewing six easy to take steps to create a BPMN diagram of your own.
This tool comes with a ton of suitable and modern futures, making it an ideal online graphic-making tool.
Now, let's draw a BPMN diagram.
Step 1: Create an Account or Sign In
The first step is always signing in to your account, but you can sign up to create one if you don't have an account yet.
Step 2: Open the BPMN Template
On the left side of your screen, you will see a blue navigation pane; click on "New" then "flowchart." A new page will load up with several design options and templates to browse through. To choose one on that page, double-click "BPMN diagram" a new page or window will be open with the selected BPMN template.
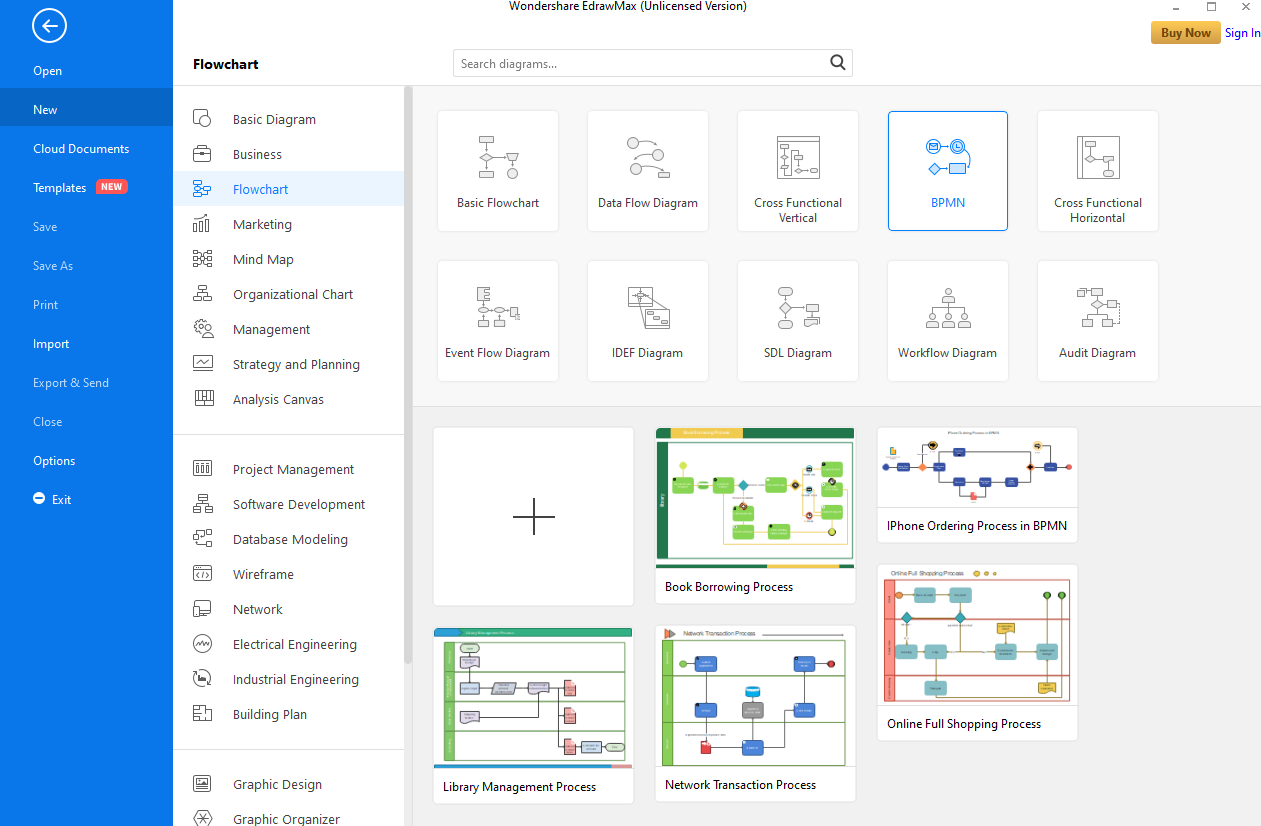
Step 3: Edit your Template
You will see a complete set of BPMN elements on the left pane that you can add to your Diagram to produce choreography, collaborations, and much more. To add them, drag and drop the elements to make flowcharts or modify your template.
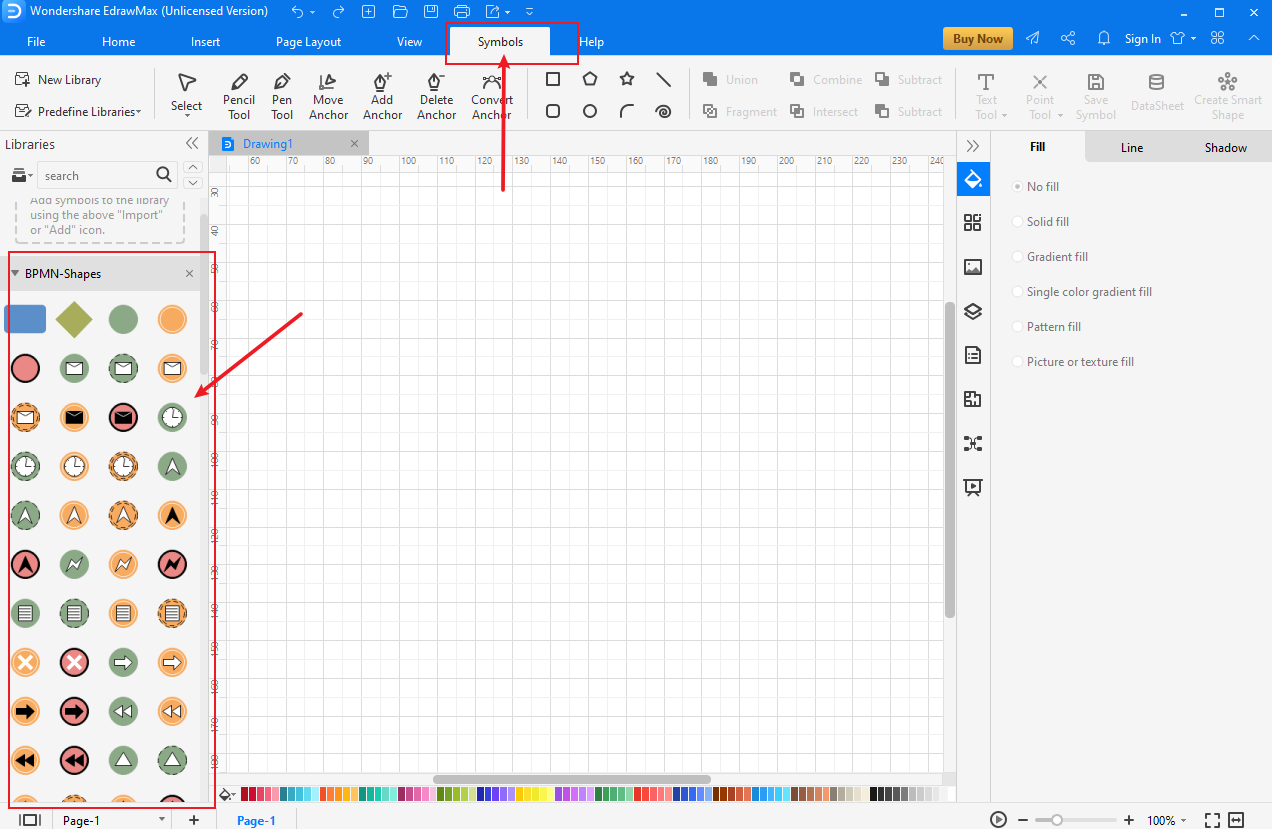
Step 4: Add Pool and BPMN Attributes
To define process participants in your Diagram, add a pool by simply dragging and dropping the shape to the drawing area. In there, you can adjust shape, size, and color to meet your requirements.
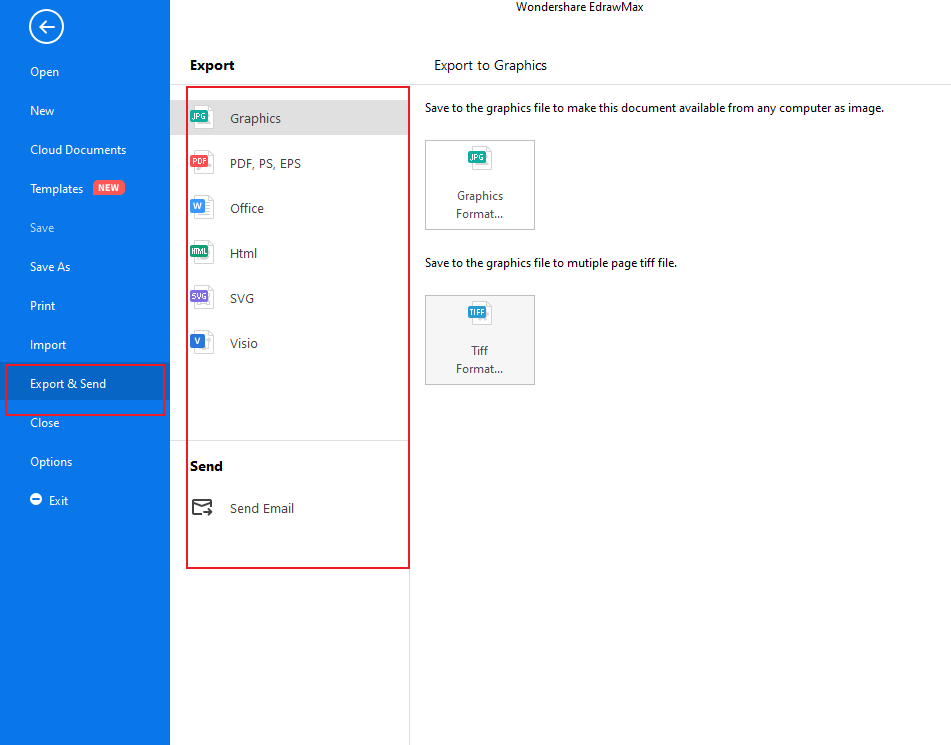
Step 5: Save and Export your Diagram
Finally, when you're satisfied with your Diagram designed and everything else, you can now save or export/share it. To save it, click on "File" at the top left corner of your screen and the "Save As," and you're done.
Tips for Making a BPMN Diagram
The following are the essential tips to creating a professional and comprehensive BPMN diagram:
- Aim at designing a BPMN diagram that fits one page
- Create a BPMN diagram with a clearly defined scope, i.e., with beginning and end
- For bigger projects, you can create different diagram versions for different stakeholders
- Before modeling a BPMN, you can start by mapping the existing business process to highlight the inefficiencies.
- To improve clarity, layout or display the data flows and associations vertically and sequence flows horizontally.
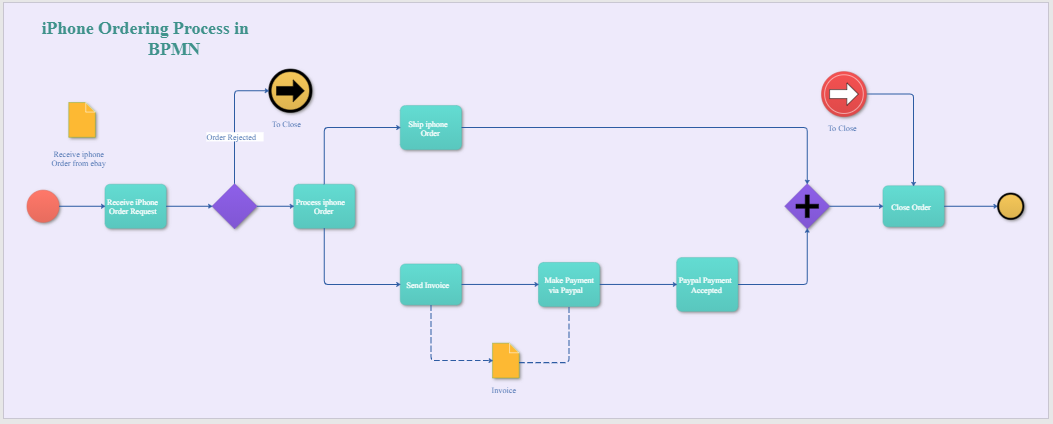
Example
The Diagram below is an excellent example of BPMN used in a business setup. The Diagram shows different levels or processes upon which eBay processes an order. The key things noticed in this BPMN diagram are:
- The two circles clearly show the start and end of the whole process.
- The Gateways are also clearly illustrated in the Diagram by the use of diamond symbols. The right-side gateway features a "+" sign in which means the gate is parallel, representing two tasks in a business flow.
- Two symbols represent the data object: the receipt from eBay and the Invoice, which are necessary data for an operation to be executed.
- The rectangles represent tasks to be done at each order processing level.