Determinants of Five Forces - How to Analyze Five Forces
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Tool
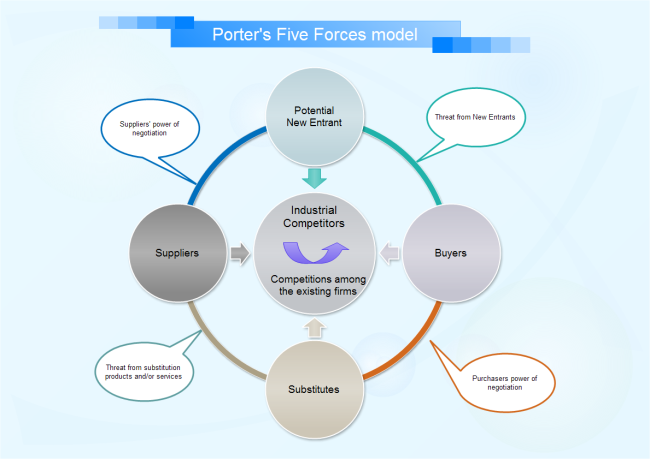
Since its introduction in 1979, Michael Porter's Five Forces has become thedefac to framework for industry analysis. The five forces measure the competitiveness of the market deriving its attractiveness. The analyst uses conclusions derived from the analysis to determine the company's risk from its industry (current or potential).
The five forces are :
(1) Threat of New Entrants,
(2) Threat of Substitute Products or Services,
(3) Bargaining Power of Buyers,
(4) Bargaining Power of Suppliers,
(5) Competitive Rivalry among Existing Firms.
Determinants of Five Forces
To analyze these five forces, there are many factors to evaluate. The following are relevant elements to consider when carrying out a Five Forces analysis.
1. Barriers to Entry:
- Economies of scale
- Proprietary product differences
- Brand identity
- Switching costs
- Capital requirement
- Access to distribution
- Government policies
- Expected retaliation
2. Determinants of Substitute Threats:
- Relative price performance of substitutes
- Switching costs
- Buyers' propensity to substitute
3. Determinants of Buyer Power
Bargaining Leverage:
- Buyer concentration versus firm concentration
- Buyer volume
- Buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs
- Buyer information
- Ability to backward integrate
- Substitute products
- Pull-through
Price Sensitivity:
- Price/total purchases
- Product differences
- Brand identity impact on quality/performance
- Buyer profits
- Decision makers' incentives
4. Determinants of Supplier Power:
- Differentiation of inputs
- Switching costs of suppliers and firms in the industry
- Impact of inputs on cost or differentiation
- Threat of backward integration by firms in the industry
Rivalry Determinants:
Five Forces Model Template
Learn how to make a five forces chart here.


