Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Five forces chart helps to determine an industry structure and the level of competition in that industry. Edraw software provides you many five forces templates to facilitate your drawing of five forces chart. Go make a five forces chart page to learn how to make a five force chart.
What are the five forces?
The five factors in Porte's five forces chart are buyer power, supplier power, competitive industry rivalry, threat of substition and threat of new entry. Analysis about these five factors help to evaluate a company's competitive position in the industry and identify what strengths or weakness can be exploited to strengthen that position.
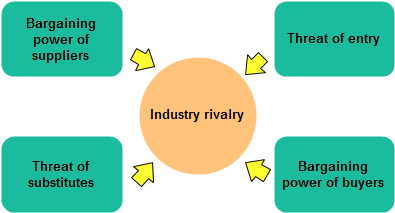
The stronger competitive forces in the industry are the less profitable it is. An industry with low barriers to enter, having few buyers and suppliers but many substitute products and competitors will be seen as very uncompetitive and thus, not so attractive due to its low profitability.
Understanding Five Forces Tool
Thefiveforcstoolisveryusefulinformulatingfirm's strategy as it reveals how powerful each of the five key forces is in a particular industry. Five forces tool is widely used to identify whether new products, services or businesses have the potential to be profitable. It can be very illuminating when used to understand the balance of power in other situations.
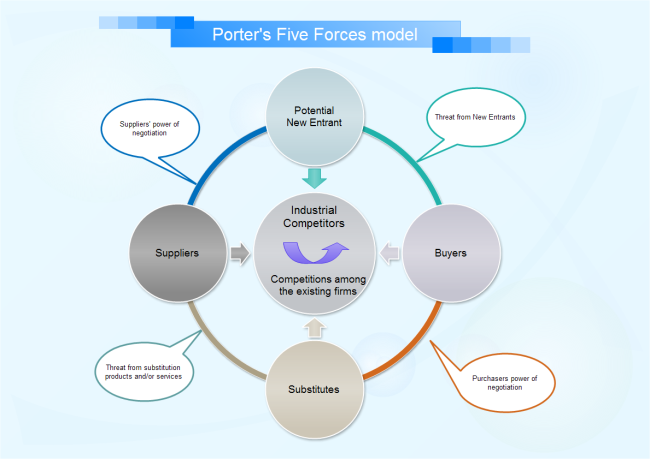
Supplier Power
A producing industry requires raw materials - labor, components, and other supplies. The term 'supplier' comprises all sources for inputs that are needed in order to provide goods or services. This requirement leads to buyer-supplier relationships between the industry and the firms that provide it the raw materials used to create products. Suppliers, if powerful, can exert an influence on the producing industry, such as selling raw materials at a high price to capture some of the industry's profits.
Strong bargaining power of suppliers allows them to sell higher priced or low quality raw materials to their buyers. This directly affects the buying firms' profits because it has to pay more for materials. Suppliers have strong bargaining power when:
- Suppliers hold scarce resources;
- Few substitute raw materials exist;
- There are few suppliers but many buyers;
- Suppliers are large and threaten to forward integrate;
- Cost of switching raw materials is especially high.

Buyer Power
The buyer power is driven by the number of buyers. It evaluates the importance of each individual buyer to your business, the cost to them of switching from your products and services to those of someone else, and so on. If you deal with few, powerful buyers, then they are often able to dictate terms to you. Buyer might have power when:
- Lots of substitute products exist;
- Suppliers operate with high fixed costs;
- Customers could produce the product themselves;
- The product is not of strategical importance for the customer;
- The customer knows about the production costs of the product;
- Switching to an alternative product is relatively simple and is not related to high costs.
Competitive Rivalry
Competitive rivalry factor describes the intensity of competition between existing companies in an industry. High competitive pressure results in pressure on prices, margins, and hence, on profitability for every single company in the industry. Competitive rivalary is the major determinant on how competitive and profitable an industry is. In competitive industry, firms have to compete aggressively for a market share, which results in low profits.

Threat of New Entry
The higher the competition in an industry, the easier it is for other companies to enter this industry. In such a situation, new entrants could change major determinants of the market environment (e.g. market shares, prices, customer loyalty) at any time. There is always a latent pressure for reaction and adjustment for existing companies in this industry.
This force determines how easy (or not) it is to enter a particular industry. If an industry is profitable and there are few barriers to enter, rivalry soon intensifies. When more organizations compete for the same market share, profits start to fall. It is essential for existing organizations to create high barriers to enter to deter new entrants.
Threat of Substitution
A threat from substitutes exists if there are alternative products with lower prices of better performance parameters for the same purpose. They could potentially attract a significant proportion of market volume and hence reduce the potential sales volume for existing players. This category also relates to complementary products. What is the likelihood that someone will switch to a competitive product or service? If the cost of switching is low, then this poses a serious threat. Here are a few factors that can affect the threat of substitutes:
- Current trends;
- Brand loyalty of customers;
- Close customer relationships;
- Switching costs for customers;
- The relative price for performance of substitutes.
Learn how to make a five forces chart here.


