Wide Area Network
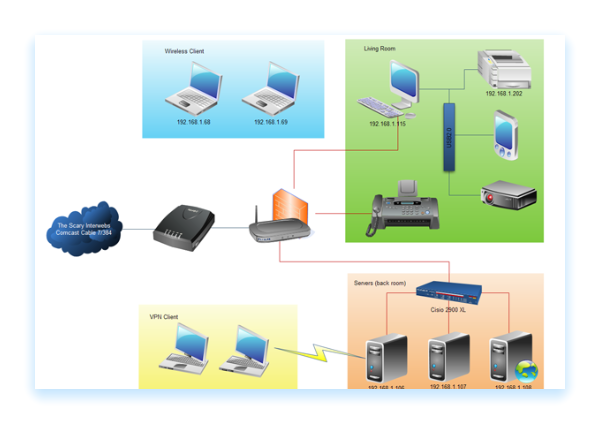
Wide Area Network Technologies
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a computer network covering multiple distance areas, which may spread across the entire world. WANs often connect multiple smaller networks, such as local area networks (LANs) or metro area networks (MANs). The world's most popular WAN is the Internet. Some segments of the Internet are also WANs in themselves. The key difference between WAN and LAN technologies is scalability. C WAN must be able to grow as needed to cover multiple cities, even countries, and continents.
A set of switches and routers are interconnected to form a Wide Area Network. The switches can be connected in different topologies, such as full mesh and half mesh. A wide area network may be privately owned or rented from a service provider, but the term usually connotes the inclusion of public (shared user) networks.
Both packet switching and circuit switching technologies are used in the WAN. Packet switching allows users to share common carrier resources so that the carrier can make more efficient use of its infrastructure. In a packet switching setup, networks have connections into the carrier's network, and many customers share the carrier's network. The carrier can then create virtual circuits between customers' sites by which packets of data are delivered from one to the other through the network.
Circuit Switching allows data connections to be established when needed and then terminated when communication is complete. This works like a normal telephone line that works for voice communication. Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a good example of circuit switching. When a router has data for a remote site, the switched circuit is initiated with the circuit number of the remote network.
Symbols of Network Architecture
Some network mapping symbols for network engineer. Provide a Common Graphics Technology for Network Mapping.
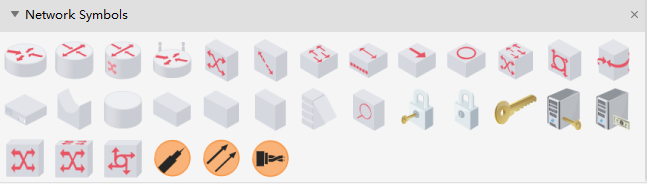


You can find more symbols for WAN diagrams here.
WAN Diagram Software
Edraw is a powerful diagramming tool helping network engineers and network designers draw wan diagrams easily and quickly. It had defined some commonly used WAN symbols in drawing WAN diagrams. Just drag and drop the pre-drawn shapes representing computers and network devices and connect them properly. An exclusive WAN diagram will be created soon!
EdrawMax
All-in-One Diagram Software
- Superior file compatibility: Import and export drawings to various file formats, such as Visio
- Cross-platform supported (Windows, Mac, Linux, Web)
Examples of Wide Area Network Technologies
|
Examples of Wide Area Network Technologies Created by Edraw! |
||
|
|
|
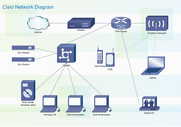
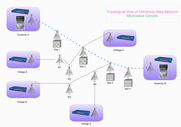
| Wide Area Network | Cisco WAN Network | WAN Topology |
Virtual private network (VPN) is a technology widely used in a public switched network (PSTN) to provide private and secured WAN for an organization. VPN uses encryption and other techniques to make it appear that the organization has a dedicated network, while making use of the shared infrastructure of the WAN.
WAN technologies generally function at the lower three layers of the OSI reference model: the physical layer, the data link layer, and the network layer. Key technologies often found in WANs include SONET, Frame Relay, X.25, ATM and PPP.
- ATM: A dedicated-connection switching technology that organizes digital data into 53-byte cell units. Individually, a cell is processed asynchronously relative to other related cells and is queued before being multiplexed over the transmission path. Speeds on ATM networks can reach 10 Gbps.
- Frame Relay: (FR). A high-speed packet-switched data communications service, similar to X.25. Frame relay is widely used for LAN-to-LAN interconnect services, and is well suited to the bursty demands of LAN environments.
- SONET/SDH: Synchronous Optical Network is an international standard for high speed communication over fiber-optic networks. The SONET establishes Optical Carrier (OC) levels from 51.8 Mbps to 10 Gbps (OC-192) or even higher. Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) is a European equivalent of SONET.
- X.25: The X.25 protocol allows computers on different public networks to communicate through an intermediary computer at the network layer level.
- PPP: A point-to-point link provides a single, pre-established WAN communications path from the customer premises through a carrier network, such as a telephone company, to a remote network. Point-to-point lines are usually leased from a carrier and thus are often called leased lines. For a point-to-point line, the carrier allocates pairs of wire and facility hardware to your line only.
IP can also be considered as a WAN technology in the packet switching environment.



