LDAP Complete Guide
Edraw Content Team
Do You Want to Make Your LDAP Diagram?
EdrawMax specializes in diagramming and visualizing. Learn from this LDAP diagram complete guide to know everything about the LDAP diagram. Just try it free now!
Lightweight directory access protocol, commonly known as an LDAP, is a protocol tool that aids in discovering data and information about a specific industry, firm, or even individuals in a network. It is also used to find valuable resources such as files, documents, and appropriate devices for that specific network. Users often incorporate Lightweight directory access protocol on private and corporate internet networks.
In today's world, there can be a hefty amount of uses for LDAP. It can be a gateway to understanding some of the ins and outs of an organization in a system. In this article, we will cover the basics and analyze some of the uses and functions of the lightweight directory access protocol.
1. What is LDAP
The lightweight directory access protocol is a cross and an open network protocol that primarily focuses on providing directory services authentication. A company, for instance, may save details about all of its devices in a database. Users may utilize LDAP to find a certain printer, identify it on the system, and discreetly access it. LDAP is commonly utilized in the development of central authentication systems. These servers store login information for all users on the network. Any apps and data can link to the LDAP server to validate and approve users.
LDAP domains often hold data that is requested frequently but hardly ever modified. As a result, LDAP is intended to provide lightning-fast READ efficiency, even for massive datasets. WRITE efficiency, on the other hand, is much lower.
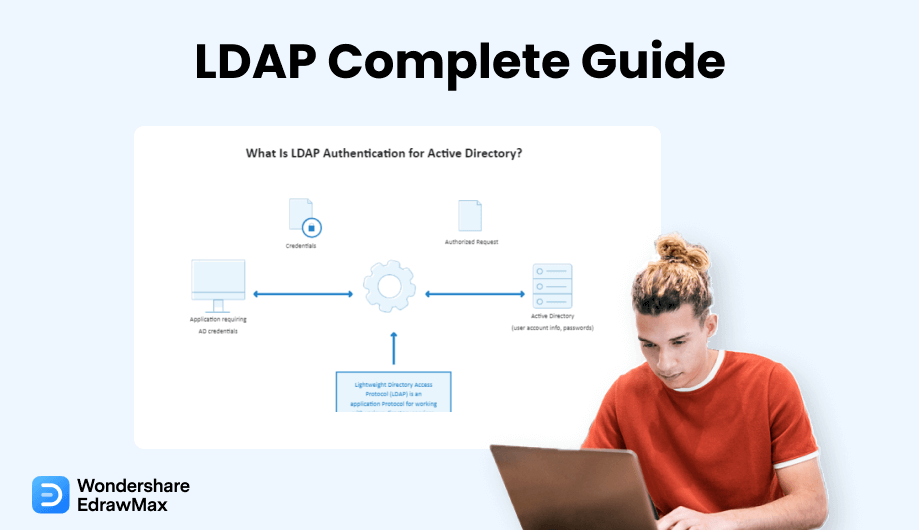
1.1 What is LDAP Authentication?
Without properly validating, a user cannot access information contained in an LDAP protocol or directories. The database stores customer, company, and authorization data and serves it to associated applications. LDAP authentication entails validating specified users and credentials by linking to an LDAP-enabled directory system. OpenDJ, OpenLDAP, and MS Active Directory are several directory systems that use LDAP.
The following is a step-by-step analysis of the authentication phase:
- The user (an LDAP-capable device or app) submits an authorization to access data in an LDAP server.
- The user gives their LDAP server login information (such as a valid password and username).
- The LDAP gateway validates the identity of the user against the fundamental user identification data in its LDAP store.
- The user can access the necessary information if the identities given match the recorded fundamental user identity.
- Invalid credentials will result in entry to the LDAP server being disallowed.
1.2 What Are the Levels of the LDAP Directory?
A common LDAP config has a "tree" classification. From top to bottom, the hierarchical levels are as follows:
- A root directory is the beginning point.
- Nations, Groups, or Businesses.
- The LDAP gateway validates the identity of the user against the fundamental user identification data in its LDAP store.
- Agencies, sections, and other organizational units.
- Individuals, documents, and linked resources (computers, prints, and so on).
An LDAP database can be distributed over many servers. With the use of replicating, client requests are scattered among different servers. Each LDAP server accepts user queries and bears responsibility for them before forwarding them to other locations. The directory will be duplicated on each server, and the subdirectories will all synchronize their contents at frequent intervals.
1.3 What Are the Uses of LDAP?
LDAP is commonly used to offer a central location for verification, which means it saves login details. LDAP may then be utilized to authenticate a user in other services and applications via a component. LDAP may be used to authenticate users and credentials with Kubernetes, Docker, Jenkins, Open VPN, and Linux Samba systems, to mention a few. The network administrator may also use LDAP solitary sign-in to obtain access to an LDAP directory. LDAP may also be utilized to add functions to a directory database system, authenticate sessions and bind them, remove LDAP elements, explore, and analyze entries using specific instructions, edit existing records, expand entries, abort requests, or deactivate operations.
If a company is unsure when to utilize LDAP, it should think about it in a few scenarios. They should think about it if:
- A particular piece of data must be located and made accessible frequently; the organization has a large number of minor data records.
- A particular piece of data must be located and made accessible frequently; the organization has a large number of minor data records.
- The company needs all minor bits of data in one specific location, and the information does not need to be well organized.
2. LDAP VS Active directory
The Active Directory, also known as the AD, functions with Microsoft Windows servers. Active Directory's primary job is to allow organizations to control privileges and limit accessibility to the connected networks. Data is saved in Active Directory as entities, which include people, parties, organizations, and resources, and these components are classified based on their identity and properties.
Microsoft created Active Directory (AD) for Windows operating systems. It is incorporated throughout most Windows OS as a spectrum of functions and processes and stores data about each registered user linked to the system. LDAP is a protocol used to retrieve and update data from Active Directory and other equivalent directory network operators. In an Active Directory, each new user contains various properties, including the user's complete identity and mail addresses. LDAP is required to extract this information in a helpful fashion.
LDAP uses an essential string-based inquiry to obtain data from Active Directory. The retrieved data (including user credentials) can be shared with linked devices or apps through LDAP. Using LDAP removes the requirement for individuals to manually type a sequence of LDAP inquiries to receive information from Active Directory. Microsoft Outlook, for instance, is an LDAP-enabled Windows software that routinely enters requests to provide you with the details you need.
LDAP
-
This protocol retrieves data from Active directory.
-
LDAP uses string-based inquiry to obtain data.
-
LDAP function on all compatible OS.
Active Directory
-
This is used to store data about registered users in the system.
-
Active Directory uses straightforward data saving process.
-
Active Directory functions only on Microsoft Windows servers.
3. LDAP VS SAML
SAML is an established protocol that enables identity providers (IdPs) to pass authorization information across service providers (SP). That language implies that you may use a single login credential to enter many services. It is easier to handle one account per person than to handle different login information to mail, CRM systems, Active Directory, and so on. SAML interactions employ Extensible Markup Language (XML) for standardized interactions between the identification administrator and internet services. SAML is the connection between a participant's identity verification and service authorization.
SAML and LDAP are as distinct as they get when it relates to domains of effect. Of course, the Lightweight directory access protocol is primarily concerned with supporting on-premises verification and other server activities. On the other hand, SAML allows users' identities to be extended to the cloud and other online apps. A significant distinction between LDAP and SAML is that most Lightweight directory access protocol server implementations are designed to be the official identity source or origin of information for identification. However, in most SAML deployments, the SAML provider is not the source of information; instead, it functions as a surrogate for a directory service, turning the authorization and verification process into a SAML-based approach.
LDAP
-
LDAP supports on-perm verifications on a specific server.
-
LDAP is the origin of information for identification.
-
LDAP functions on a single solitary server.
SAML
-
SAML allows users to extend cloud and other online applications.
-
SAML serves as a surrogate for directory services.
-
SAML can be incorporated in multiple servers.
4. LDAP Operation Types
When talking about some of the operations of LDAP, ten primary operations are mandatory to know to understand LDAP processes fully. They are:
4.1 Bind
Bind functions are used to authorize clients (as well as the individuals or tools that they represent) to the network device, to create a registration identity that will be used for successive activities performed on that links, and to define the Lightweight directory access protocol version that the user will be using. Lightweight directory access protocol bind responses allow you to utilize either primary or SASL verification. The DN of the record recognizes the account to validate for that user in primary verification, and the evidence identification is in sort of a passcode. Because the credential is sent without encryption, it is strongly advised that primary verification be used only over an encrypted channel.
4.2 Search
Clients can use this procedure to browse for and read information. You may look for items by description, volume, reach, category, and other characteristics. The comparison tool lets you quickly determine whether a specified entry has properties.
4.3 Compare
An LDAP comparison function can be utilized to detect whether a provided record has a specific data point. A comparison request has the following elements:
- The DN of the record for which a decision is to be taken.
- The user gives their LDAP server login information (such as a valid password and username).
- The characteristic specification (the characteristic type of title and zero or more characteristic alternatives) for which the decision is to be made.
- The statement results in which the decision is to be made.
- When the comparison procedure is finished, the server will produce a simple response with an outcome result and potentially paired DN, diagnostic information, references, and/or response parameters.
4.4 Add
An add function can be utilized to establish a new record in the DIT. An add query contains the DN of the record to be created and the characteristics that should be included in that record. The collection of attributes must contain the objectClass property, which specifies which object classes should be included in the entry, as well as any characteristics needed by such object categories and related DIT content rules. The characteristics used in the RDN of the record must be included in the item, but the host should also include them even when they are not included in the additional query.
4.5 Delete
To eliminate an object from a directory system, perform the delete procedure. The DN of the record to be removed is the only component in the delete query. In most circumstances, the intended record must be a leaf node (one that has no successors). However, specific systems may enable the insertion of a subtree to delete query restriction to enable an element to be destroyed along with its superiors. When a delete function is finished, the network will provide a simple response with an outcome number and optional matching DN, diagnostic information, links, and/or response parameters.
4.6 Modify
A modify function could be used to change the information of a current directory service record. A solitary modification function could include problems that influence distinct characteristics (Until those characteristics are all in the same registration). All those modifications will be analyzed atomically, which means they will all fail or succeed as a component. The node will not reveal the inclusion in a partially modified position. Any modification that would eventually eliminate any characteristic value utilized in the RDN cannot be modified with a modified procedure; any modification that might affect an entry's DN must be made with an updated DN operating condition.
4.7 Modify DN
A modified DN action can be performed to change the Domain of an existing server record. This may entail updating the RDN for the record and/or relocating the entry inside the DIT. Even though the LDAP standard does not prohibit altering and/or relocating an element with subordinate values, some directory systems may not enable or put limits on such actions.
4.8 Unbind
An unbind procedure informs the directory system that the user is preparing to disconnect from the server. When the server receives this response, it should kill its contact with the user. The link is no longer functional, even if the user refuses to quit after delivering the unbind application. An unbind query has no components, and there is no reply statement to be delivered in return to an unbinding query. Although the action's name implies that it is parallel to the bind function, it does not simply return the link to an unverified phase. An unbind function invalidates the network, so neither the user nor the gateway should endeavor to communicate further over a link upon which unbind function has been performed. If a client wants to restore an unauthenticated link, it should execute an anonymized simple bind on that connected device.
4.9 Abandon
The Lightweight directory access protocol is asynchronous. While many users submit an LDAP query and then wait for the response before submitting the following query, this is not necessary. Several Lightweight directory access queries can be issued over the identical link so that the client can analyze them simultaneously. Then the responses can be received when they are provided by the client, perhaps in a reverse context than the related queries were sent. There is no reply to an abort request, and there is really no certainty that the host would be able to honor that demand. The action may still finish, so if it is a write function, the modifications included with the demand may still be implemented. If the function wraps up after an abort is obtained, the client may or may not provide a reply. Therefore, the absence of a reply should not be regarded as an indicator that the process was aborted.
4.10 Extend
LDAPv3 is an expandable framework that may be used to achieve tasks that were not anticipated when the specifications were published. One of the key methods for accomplishing this is by using extended functions. The associated extended result contains all of the components of a basic Lightweight result (such as a necessary result protocol and selectable paired DN, diagnostic text, consultations, and reply controls), but it also may encompass an additional OID to determine the form of reply text and an additional valuation that included an encrypted illustration of extra information about the coding that was executed.
5. Pros and Cons of LDAP
Before we start talking about the disadvantages of LDAP, let us talk about some of the advantages that make LDAP that can be beneficial for an organization or the group that may incorporate LDAP in their systems.
Pros of using LDAP:
-
It is open-source: It rarely costs anything at all to acquire and test OpenLDAP.
-
It serves as a standard protocol: RFC 2251 approved the Lightweight directory access protocol as an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) specification in 1997. As a result, the market promotes and will keep supporting LDAP.
-
LDAP is flexible: Lightweight directory access protocol authentication is used by programmers and IT administrators for various purposes, notably app and remote data authentication. And, even though it has been utilized in so many several ways, there is indeed a community that helps individuals get the most from it.
-
Compatibility: LDAP is designed to be interoperable with a wide range of os and platforms. Different LDAP services, nevertheless, may limit this versatility; for instance, AD is Windows-centric and frequently necessitates add-ons to integrate effectively with other OS systems.
-
Security features: LDAP was originally communicated in text format; nevertheless, there are methods for encrypting LDAP connections, either over TLS (STARTTLS) or over the SSL (LDAPS). STARTTLS is the best and most secure solution, with LDAPS coming in a close second.
Cons of using LDAP:
-
The age factor: LDAP is an outdated protocol. SAML and other newer authentication methods are designed for contemporary, cloud-forward Computing settings that utilize online applications.
-
Permissions are mandatory: LDAP is set up on-prems using an OpenLDAP system, which is an arduous task. Setting up an on-prems authentication system that connects to online IT services is less than desirable for enterprises migrating to the cloud.
-
The need for an expert: In most cases, LDAP configuration and operation require the assistance of a professional. Individuals with this degree of technical expertise can be hard to come by and are costly to hire. This is particularly applicable for OpenLDAP.
-
The ramp-up factor: The greater the size of your firm, the more complicated it is to establish new directories. Since directories are fundamentally an aggregation of all the elements in your organization, creating new directories from the start or pivoting from one directory to another would be difficult.
6. How Does LDAP Work?
LDAP defines a technique of directory management that permits the addition, deletion, and modification of entries, as well as the retrieval of those data to ease user authentication and authorization to services.
In order to create the LDAP using traditional ways, you need to follow the steps below:
Step 1: Update
Any information that is available on the LDAP system needs to be updated frequently for the system to work and function effectively. This process includes adding, modifying, and deleting data in the directories.
Step 2: Registering a query
To start working on the LDAP services, individuals need to provide a query to the system. This query can contain an action such as searching or comparing the data that is available in the registered directories.
Step 3: The Authentication
Bind and unbind are the primary authentication operations; abort, a third action can be used to prevent a client from performing an assignment.
7. How to Draw an LDAP Diagram in EdrawMax
Drawing an LDAP diagram is a straightforward process when working on EdrawMax and can be extremely useful for businesses in achieving the desired actions. EdrawMax is well equipped to design a LDAP Diagram. There are only a couple of steps that you need to follow in order to easily create it, like:
Step1 Open EdrawMax and Login
The very first step that you need to follow is to install EdrawMax in your system. Go to EdrawMax Download and download the network diagram software depending upon your operating system. If you need remote collaboration with your office team, head to EdrawMax Online and log in using your registered email address.
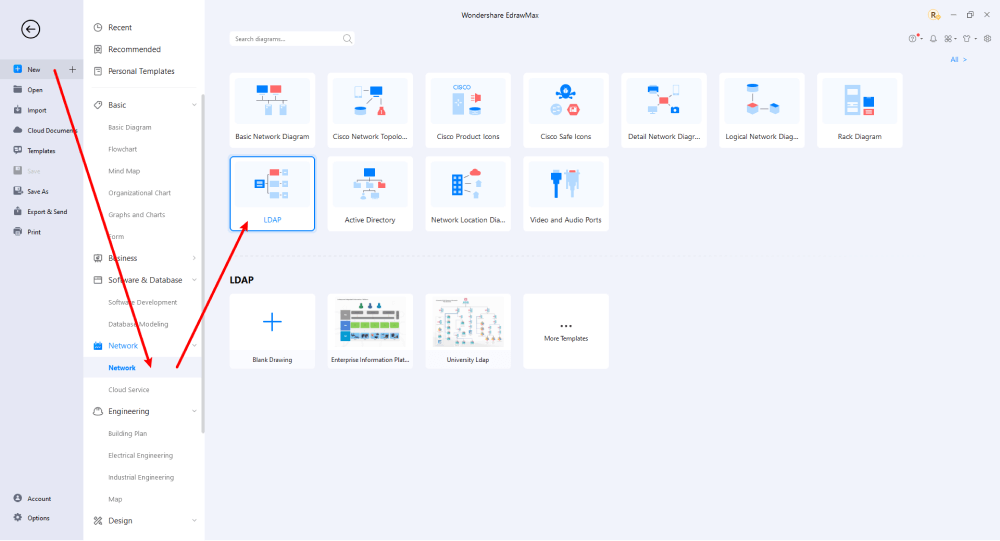
Step2 Select a Template
After launching, the Home screen opens by default. Head to the Template bar and search for Network Diagrams in the search box. In-built templates specific to your search will appear on the screen. EdrawMax features a large library of templates. We have more than 25 million registered users who have produced thorough Templates Community for each design. Select the template you like and click Use Immediately to open it in a new window for customization.
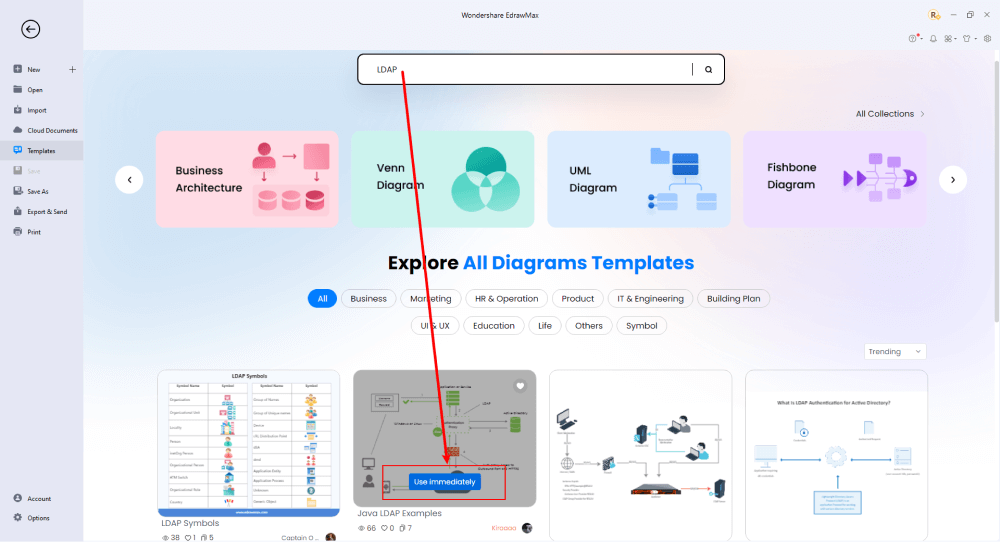
Step3 Create From Scratch
From the EdrawMax homepage, you will find the '+' sign that takes you right to the canvas board, from where you can start designing the network diagram from scratch. Coupled with your technical expertise, you can use a wide range of symbols to draw a detailed network diagram.
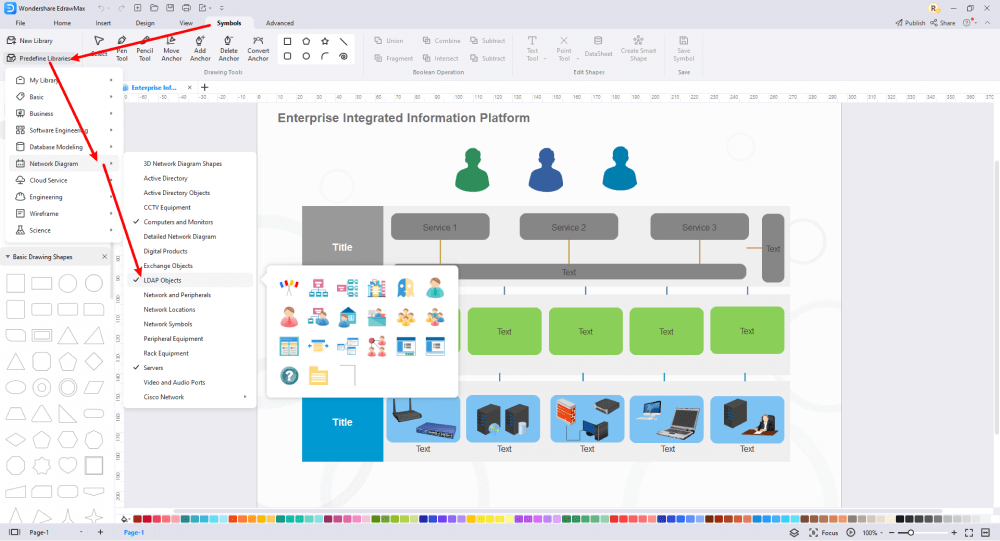
Step4 Select Symbols
EdrawMax includes a large number of symbol libraries. You may quickly build any type of diagram with over 26,000 vector-enabled symbols. If you can't locate the symbols you need, you can easily import some images/icons or build your own shape and save it as a symbol for later use. Simply go to the 'Symbols' part of EdrawMax and select the 'Predefined Symbol' section from the top toolbar. Hundreds of symbol categories are accessible for you to utilize and incorporate into your LDAP diagram.
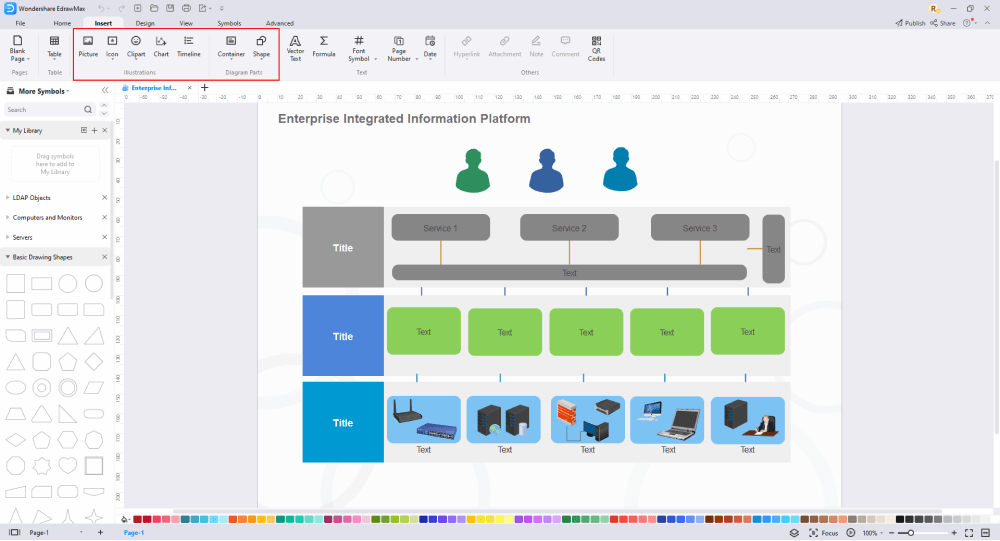
Step5 Add Components
After you have sketched out the basic pieces, you may customize the typefaces, colors, and other details by selecting the right or top menu to make your LDAP design more visually appealing. Also, feel free to draw ideas from other layouts on Templates Community and transfer some of the photos or features that you think would go well with your LDAP design.
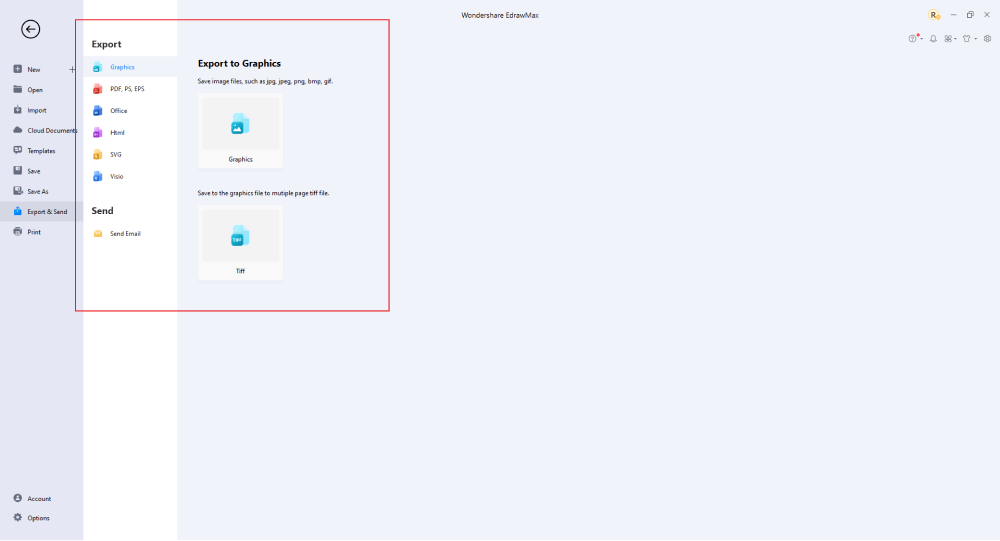
Step6 Wrap it up
Once the LDAP design is complete, you may engage with your workgroup to get their feedback by using our Cloud-based files; for one LDAP example, everyone gets free 100M cloud services. EdrawMax supports exporting data into a variety of categories, including Graphics, Microsoft Office, HTML, PDF, Visio, and others. You can also share via social networks or emails. You can also print it or display it to others by utilizing "Presentation Mode."
Basically, it is simple to create an LDAP diagram in EdrawMax, just grab a template and keep customizing, drag and drop professinal LDAP symbols to make your drawing better. If you are still confusing about how to make an LDAP diagram in EdrawMax, you can find more tutorial videos from our Youtube.
8. Free LDAP Diagram Software
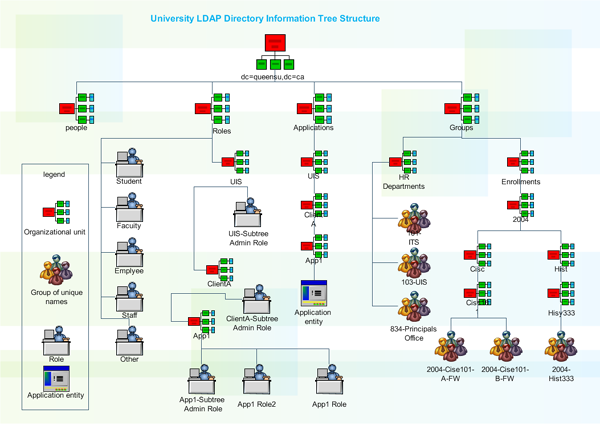
Managing a computer network today is no small task. In addition to controlling access to printers and files over the network, most administrators must also manage security and access, optimize traffic flow across Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs), coordinate repair and maintenance of network equipment, and oversee data backup, storage, and recovery. LDAP Directory Services applications, such as iPlanet's Directory Server, provide a central location for managing network assets, such as computers, users, groups, and so on. Those assets are organized into a hierarchical tree structure, which is typically viewed in a small editing window.
Although this view of the directory can be simple to use, it does not provide a clear high-level diagram of the directory structure, and most importantly cannot be printed. The Edraw LDAP Directory Services solution provides administrators with clear, detailed representations of current and proposed directory structures, which can be viewed, printed, and presented to management for planning new networks, coordinating migrations, and for documenting existing networks. Figure 1 shows a typical directory service application interface.
EdrawMax, One of the best LDAP diagram software, makes outlining, creating effective templates for business, drawing, and much more straightforward and compelling. With thousands of options, EdrawMax can deliver the best LDAP templates that can visually make your business presentations attractive and stunning. Let us now see some of the features that can be utilized in developing the best LDAP diagram.
The best EdrawMax features that can assist you in your LDAP diagram:
- The sophistication of the interface of the diagram tool determines whether consumers plan to utilize it. EdrawMax is notable for its simple interface, which makes it easy for beginners to use.
- While diagramming, you may produce the latest ideas for your task. The note option is ideal for jotting down all your ideas.
- Because the interconnection in the design is like a branch on a tree, it is critical for you. EdrawMax enables connections to intuitively match things up with various forms.
- Provide 25 distinct color variations created by experienced designers for non-designers; consequently, it is time to personalize your design.
- Apart from the planned layout, an eye-catching infographic or chart must be decorated with wonderful symbols to communicate your originality.
- You can now quickly create slideshows using EdrawMax's slideshow generator. It assists the user by choosing, highlighting, and displaying everything available in the group presentation.
9. Final Thoughts
And there you have it! A detailed guide on LDAP, its uses, and benefits. Always make sure to develop an understanding LDAP diagram so that everyone in the group can relate to and work efficiently on LDAP servers. Though there are some drawbacks, make it a point to create a problem-solving diagram using EdrawMax, and see the uplift in the productivity of your business!
The moment you start using EdrawMax , you will realize that the tool comes with several amazing features that ease your efforts in creating the LDAP diagrams and help you share the designs using the easy sharing option. With EdrawMax, you can export your file into multiple formats, and share your works on different social media platforms, like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Pinterest. All in all, EdrawMax is a wonderful tool that caters to all of your designing and drawing needs.
Network Diagram Complete Guide
Check this complete guide to know everything about the network diagram, like network diagram types, network diagram symbols, and how to make a network diagram.
You May Also Like
Blueprint Complete Guide
Knowledge
Building Plan Complete Guide
Knowledge
Evacuation Plan Complete Guide
Knowledge
Fire Escape Plan Complete Guide
Knowledge
Floor Plan Complete Guide
Knowledge
Store Layout Complete Guide
Knowledge


